THE MEANING Û TEXT THEORY: DEPENDENCY TREES
Another important feature of the MTT is the use of its dependency trees, for description of syntactic links between words in a sentence. Just the set of these links forms the representation of a sentence at the syntactic level within this approach.
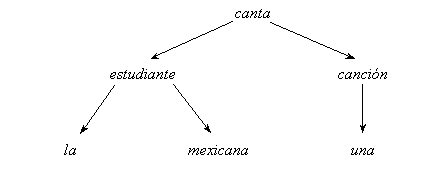 FIGURE II.2. Example of a dependency tree.
FIGURE II.2. Example of a dependency tree.
|
For example, the Spanish sentence La estudiante mexicana canta una canción can be represented by the dependency tree shown in Figure II.2. One can see that the dependency tree significantly differs from the constituency tree for the same sentence (cf. Figure II.1).
Up to the present, the proper description of the word order and word agreement in many languages including Spanish can be accomplished easier by means of the MTT. Moreover, it was shown that in many languages there exist disrupt and non-projective constructions, which cannot be represented through constituency trees or nested structures, but dependency trees can represent them easily.
In fact, dependency trees appeared as an object of linguistic research in the works of Lucien Tesnière, in 1950ís. Even earlier, dependencies between words were informally used in descriptions of various languages, including Spanish. However, just the MTT has given strict definition to dependency trees. The dependency links were classified for surface and deep syntactic levels separately. They were also theoretically isolated from links of morphologic inter-word agreement so important for Spanish.
With dependency trees, descriptions of the relationships between the words constituting a sentence and of the order of these words in the sentence were separated from each other. Thus, the links between words and the order in which they appear in a sentence were proposed to be investigated apart, and relevant problems of both analysis and synthesis are solved now separately.
Hence, the MTT in its syntactic aspect can be called dependency approach, as contrasted to the constituency approach overviewed above. In the dependency approach, there is no problem for representing the structure of English interrogative sentences (cf. page 39). Thus, there is no necessity in the transformations of Chomskian type.
To barely characterize the MTT as a kind of dependency approach is to extremely simplify the whole picture. Nevertheless, this book presents the information permitting to conceive other aspects of the MTT.