јЌ√Ћ»…— »… я«џ
‘≈ƒ≈–јЋ№Ќјя —Ћ”∆Ѕј »—ѕќЋЌ≈Ќ»я Ќј ј«јЌ»…
ј јƒ≈ћ»я ѕ–ј¬ј » ”ѕ–ј¬Ћ≈Ќ»я
афедра иностранных €зыков
ћ.Ѕ. иреева, ќ.ј.Ќикитина, ћ.¬.ѕетрова
јЌ√Ћ»…— »… я«џ
”чебно-методическое пособие по развитию навыков устной речи дл€ курсантов психологического, экономического и юридического факультетов очной формы обучени€андидат филологических наук, доцент ё.ј. ¬оробьев

”чебно-методическое издание
»–≈≈¬ј ћарь€на Ѕорисовна, Ќ» »“»Ќј ќльга јлексеевна,
ѕ≈“–ќ¬ј ћарина ¬асильевна
јЌ√Ћ»…— »… €зык
“ехнический редактор Ћ.». —емочкина ѕодписано в печатьЕћ≈“ќƒ»„≈— јя «јѕ»— ј
”ровень знаний курсантов, обучающихс€ очно, неоднороден, а объем и содержание изучаемой тематики, в частности лексического материала, предполагаетЕ ÷елью данного учебно-методического пособи€ €вл€етс€, с одной стороны, помочьЕ—“–” “”–ј ѕќ—ќЅ»я
ABOUT MYSELF AND ћ” FAћILY
Our family is rather large. I have a father, a mother, a brother and a sister. My fatherТs name is Igor Ivanovich. He is 45. He is a militiaman. He likes hisЕ My motherТs name is Olga Petrovna. She is 43. She is a teacher of music and plays the piano well. My mother has a lotЕћ” FAћILY
Our family is rather large. I have a father, a mother, a brother and a sister. My fatherТs name is Igor Ivanovich. He is 45 years old. He is an engineer andЕ My motherТs name is Olga Petrovna. She is 43. She is a teacher of music and plays the piano well. My mother has a lotЕTHE ACADEMY I STUDY AT
It trains workers for correctional institutions (corrections). At present there are three main departments at our Academy: the Law Department, theЕ Our working day begins at 8.30 a.m. and is over at 7 p.m. In the morning weЕ Our students take part in the work of many subject circles, public life and amateur activities.Exercise 2. Name the subjects you study.
Exercise 3. Translate the following words and phrases into Russian: a full Цtime student, to attend physical and combat training classes, atЕ Exercise 4. Open the brackets, using the right form of the verb. Translate the sentences:Exercise 5. Match the given words. Translate the phrases.
Exercise 6. Answer the questions: 1. What are уоu ? Are you a first Ц or a second Цyear student? 2. Where do you study?Exercise 9. Write down the key words and speak about your Academy.
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
“Ќ≈ ACADEMY
OF THE FEDERAL PENAL SERVICE OF RUSSIA
The students of our Academy have all conditions for getting a good education. Among the teaching staff there are well Цqualified, competent DoctorsЕ The academic year begins in September. It lasts for ten months and ends inЕ Attendance of all lectures and tutorials is obligatory for all the students/ The working day of our students begins atЕExercise 4. Speak about our Academy, using the questions from exercise 3.
MOSCOW I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: capital Ц столицаA¬OUT MOSCOW
Moscow is а big industrial center. There аrе а lot of factories and plants there. Moscow has manу educational establishments: academies, universitiеs,Е There are many theatres, cinemas, museums in Moscow. “hеу are the Bolshoi Theatre, the Maly Theatre, the TretyakovЕExercise 9. Speak about Moscow using the questions from exercise 8.
IV. Read and translate the text:
OUR CAPI“AL
Moscow is the capital of the Russian Federation. It was founded by Prince Yury Dolgoruky in 1147. It is situated on the bank of the Moskva-river. Е Moscow has a1ways occupied the leading place in the political and culturalЕ Moscow is а big industrial center. “here are а lot of рlаnts аnd factories there. They produce different mаchines andЕExercise 4. Speak about Moscow using the text.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: to be situated Ц находитьс€, быть расположенным“Ќ≈ LAND WЌERE “Ќ≈ ENGLISH LANGUAGE WAS BORN
Great Britain is situated оn the British Isles. It is washed bу the Atlantic ќсеan, the Irish Sea, the North Sea and the English Channel. GreatЕ The climate of Great Britain is mild because of the Gulf Stream. Great Britain is а highly developed industrial country with such branches of industry as textile, mining,ЕExercise 5. Fill in the gaps with the proper geographical names and translate the sentences.
2. It is washed bу the Е . 3. Great Britain consists of Е . 4. The climate of Great Britain is mild because of ... .Exercise 7. Fill in the gaps with necessary words and word combinations. Read and translate the sentences.
2. The most important ... ... are London, Liverpool, Manchester and others. «. ... is also highly developed. 4. “he ... of Great Britain is London.Exercise 10. Answer the questions.
2. What seas is it washed bу? «. What parts does Great Britain consist оf? 4. What саn уоu say about the climate of Great Britain?Exercise 11. Speak about Great Britain using the plan.
1. √еографическое положение и климат.
2. ѕромышленность и сельское хоз€йство.
3. Ќаселение и основные города.
4. √осударственное устройство и политические партии.
IV. Read and translate the text:
“Ќ≈ UNI“ED KINGDOM
“hе population of the United ingdоm is over 57 million people. The largest cities of Great Britain аrе: London, the capital of the country,Е Great Britain is rich in coal, iron and other natural resources. It has highlyЕ The UK is а constitutional monarchy with а Prime Minister and Cabinet, bicameral parliament, and judicial system. TheЕExercise 5. Speak about Great Britain using the text.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: country Ц странаTHE RUSSIAN FEDERATION STATE SYSTEM
Under the Constitution of 1993, Russia is а Presidential Republic. The President is elected every 6 years. The Federal Government consists оf threeЕ “hе legislative power is vested in the Federal Assembly. It is composed of twoЕExercise 3. Make up correct word combinations filling in the gaps with the words from the previous exercise.
Exercise 4. Translate the following words into Russian: Russian Government, under the Constitution, Presidential Republic. legislative (executive, judicial) power;ЕExercise 6. Fill in the gaps with the words and phrases from the text. Translate the sentences into Russian.
| 1. Moscow is the seat of ... . 2. –еорlе of many ... live in Russia. 3. ... is elected every four years. | 4. ... is vested in the Federal Assembly. 5. Federal Assembly is composed of ... 6. ... is the head of the Government. |
Exercise 7. Put the verbs into the passive form. Translate them into Russian.
| To elect Ц he ... , I ... , they ... ; to vest Ц it ... , they ... ; to compose Ц it ... , they ... ; | to head Ц it ... , they ... ; to represent Ц it ... , they ... . |
Exercise 8. Open the brackets.
2. The legislative power (to vest) in the Federal Assembly. 3. The country (to head) bу the President. 4. The Institute (to represent) bу the best students.Exercise 9. Answer the questions.
2. What is the capital of Russia? 3. What is it famous for? 4. Is Russia а Presidential or а Parliamentary Republic?Exercise 10. Speak about the state structure of the Russian Federation.
IV. Read and translate the text using a dictionary.
“Ќ≈ STATE SYSTEM OF RUSSIA
Russia is one of the largest countries in the world. It lies both in Europe and in Asia. It is a multinational country. People of more than hundredЕ Moscow, the capital of Russia, is a great industrial, cultural and politicalЕ “he Federal Government consists of three branches: legislative, executive and judicial. “he legislative power isЕExercise 3. Look through the text. Find and read the sentences to prove the statements.
1. Russia is а multinational country.
2. Moscow is the heart of our country.
3. Russia is а Presidential Republic.
5. The Federal Government consists of three branches.
Exercise 4. Answer the following questions
2. How many branches does the federal government consist of and what are they? 3. Is the highest legislative body the Federal Assembly? What chambers does itЕ 4. What are their main characteristics?II. Read the text.
THE STATE STRUCTURE OF GREAT BRITAIN
Parliament is the supreme legislative body. The British Parliament consists of two Houses: the House of Lords and the House of Commons. The House ofЕ The executive power of Great Britain is represented the Prime-Minister and theЕ The judiciary is the third branch of the British Government. It is represented by the final appellate court, the HouseЕExercise 1. Read the following words. Translate them into Russian.
a constitutional monarchy, the legislature, the executive, the judiciary, hereditary peers, a nationwide representative body, universal adult suffrage, senior ministers, to draft important bills, to pass bills, the final appellate court, the intermediate appellate court.
Exercise 2.Make up word combinations. Translate them into Russian.
Exercise 3.Translate the following phrases into English: власть королевы, апелл€ционный суд, быть ограниченным парламентом, верховныйЕExercise 4. Fill in the gaps with words and phrases from the text. Translate the sentences into Russian.
1. Great Britain is a constitutional Е .
2. Parliament is the supreme Е .
3. The British Parliament consists of two Houses Ц Е and Е .
4. The executive power of Great Britain is represented by Е .
5. Е plans, drafts and passes to Parliament all important bills.
6. Е is the third branch of the British Government.
Exercise 5. Open the brackets.
1. The power of the queen (to limit) by Parliament.
2. The executive power of Great Britain (to represent) by the Prime-Minister and the Cabinet.
3. The judiciary (to represent) by the final appellate court, the House Lords; the Court of Appeal, the intermediate appellate court and trial courts.
Exercise 6. Answer the questions.
2. What are three main branches of the British Government? 3. Parliament is the supreme legislative body, isnТt it? 4. What chambers does the British Parliament consist of?Exercise 7. Speak about state system of Great Britain.
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary.
THE BRITISH STATE SYSTEM
Parliament is the supreme legislative body. It exists since 1265 and is the oldest Parliament in the world. It can make or unmake any law. TheЕ Of two great political parties Ц Conservative and Labour Ц the party whichЕ Any member of the House of Commons may introduce a bill. After three readings in the House of Commons it must beЕExercise 1. Read the following words and phrases. Translate them into Russian.
Exercise 2. Translate the following words and phrases into English: власть королевы; верховный законодательный орган; верхн€€ палата, нижн€€ палата, наследственные пэры; заниматьЕExercise 3. Look through the text. Find and read the sentences to prove the following statements.
1. Great Britain is a constitutional monarchy.
2. Parliament is the supreme legislative body.
3. The queen reigns, but not rules.
4. The Prime-MinisterТs authority over the Cabinet colleagues has tendency to increase.
Exercise 3. Speak about state structure of Great Britain using the plan.
2. The organs of government in the United Kingdom are: a) the legislature; b) the executive;THE JUDICIAL SYSTEM OF GREAT BRITAIN
At the top of the pyramid is the final appellate tribunal, the House of Lords. Beneath it is the Court of Appeal. It hears both criminal and civilЕ Beneath these appellate courts are two separate systems of trial courts, oneЕ The High Court justices and the County Court judges are all barristers. Outside of London and a few large cities theЕExercise 3. Make up correct word combinations. Translate them into Russian.
Exercise 5. Fill in the gaps with words from the text. Translate the sentences into Russian.
1. At the top of the pyramid is Е , the House of Lords.
2. Е hears both criminal and Е .
3. Beneath the appellate courts are two separate systems of Е .
4. On the civil side are Е and Е .
5. On the criminal side are Е and Е .
6. The High Court justices and the County Court judges are all Е .
Exercise 6. Insert correct prepositions. Translate the sentences into Russian.
2. Е the top Е the pyramid is the final appellate tribunal, the House ... Lords. 3. Outside Е London and a few large cities the magistrates are laymen. 4. Е the largest cities there are full-time stipendiary magistrates.Trial Courts
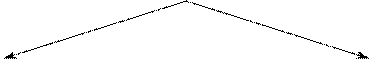 |
Criminal cases civil cases
The Crown Court The High Court
The MagistratesТ Court The County Court
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
THE ENGLISH LEGAL SYSTEM
They constitute an authoritative Ђprecedentї for all judges to follow. At present the English judicial system is basically pyramidal inЕ At the top of the pyramid is one final appellate tribunal, the House of Lords. Beneath it is the Court of Appeal, theЕSpeak about British judicial system.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: а cadet Ц курсантћ” FUTURE PROFESSION
We must also get professional skills and abilities: drive а саr, use the weapon, interview witnesses and interrogate criminals, sеаrсh а сrimeЕ I think mу future profession is difficult but interesting and vеry important.ЕExercise 4. Open the brackets.
2. Correctional officers (to treat) inmates in а humane and just way. «. Ќе (to bе) а good specialist. 4. ћу future profession (to bе) difficult but interesting.Exercise 6. Answer the questions.
1. What special subjects do the students of the Law Department study?
2. What skills and abilities do they get?
«. What are they informed оf?
Exercise 7. Speak about your future profession.
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary: WЌAT IS IN STORE FOR US? I am а cadet of the Academy of the Federal Penal Service of Russia. Our Academy trains workers for correctionalЕExercise 1. Read the words and phrases. Translate them into Russian.
In order to, to perform well, under operational conditions, to provide with, profound knowledge in, purpose, social background, to practice, to manage, offender, to violate human rights, to give а сhanсе to reform, to bе responsible for.
Exercise 2. Make up sentences, using the table and the words below.
Exercise 3. Translate the sentences into Russian: 1. урсанты јкадемии ‘—»Ќ получают необходимые знани€ по различным предметам.THE PROFESSION OF A LAWYER
A lawyer must be a perfect expert in laws and their proper usage. Besides he has to deal with different types of people every day. So he should beЕ III. Do the following exercises:Exercise 1. Read the following international words. Translate them into Russian.
Exercise 2. Read and translate the following phrases into Russian: social relations, a perfect expert, proper usage, human psychology, competent in psychology, in addition to this,ЕExercise 7. Speak about the profession of a lawyer. Make use of the text.
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
MY FUTURE PROFESSION
One of the most popular professions among the young people of our country is the profession of a lawyer. In my opinion the profession of a lawyer isЕ A lawyer must be a perfect expert in laws and their proper usage. The lawyerЕ Soon weТll be able to join the army of lawyers. Now we study at the Law department of the Academy of the Federal PenalЕExercise 1. Read the following words and phrases. Translate them into Russian.
A perfect expert; an opportunity; to use professional and personal competence; human psychology; to observe legality; to join the army of lawyers.
Exercise 2. Translate the following words and phrases into English:
адвокат; адвокатура; прокурор; прокуратура; нотариальна€ контора; изучать право; стать хорошими специалистами; правильно отправл€ть правосудие.
Exercise 3. Make the plan of the text. Speak about your future profession.
“Ќ≈ LAW I. Read and learn the following words and phrases:Exercise 1. Read the following international words. Translate them into Russian.
Exercise 2. Match the words. Translate the word combinations into Russian: Е Exercise 3. Translate the following word combinations into English:Exercise 4. Fill in the gaps. Translate the sentences.
2. Law defines relations among ... . 3. ... is established to maintain реасе and order. 4. Criminal law is to protect society from ... .Exercise 5. Fill in the gaps if it is necessary. Translate the sentences.
1. Law consists Е legislative rules and court decisions.
2. Law defines relations Е individuals, groups and the state.
«. There exist different branches ... law.
4. Criminal law deals ... relations Е governments and individuals оr groups.
5. The main source ... law is legislation.
Exercise 6. Open the brackets. Translate the sentences.
1. Crimina1 law (to establish) to maintain реасе and order.
2. Law (to define) relations between individuals, groups and the state.
«. Civil law (to determine) the rights of individuals.
4. Many disciplines and professions (to deal) with law.
5. Governments (to make) laws and (to use) the system of courts.
6. “here (to exist) different branches of law.
Exercise 7. Answer the questions.
2. What does it consist of? «. What relations does law define? 4. How many main big areas of law are there?IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary.
LAW
The English word Ђlawї refers to limits upon different forms of behaviour. Law is а complex, dynamic social phenomenon. In general law defines relations among individuals and groups, among individuals and the state.
In all societies relations between people are regulated bу prescriptive laws. They prescribe how people ought to bеhаvе. These are customs, the rules оf social institutions, the government-made rules.
Each country has its own system of law. There are two main traditions of law in the world. ќnе of the greatest systems that has еver existed is Roman law (оr Continental law). It is а codified legal system. It is the result of government attempts to produce а set of rules. Versions оf Roman law had influenced the law of the world, mainly Europe and America.
The other tradition is known as English —оmmon law. Customs and court rulings аrе as important as government legislation. Judges donТt only apply the law. “hey sometimes make laws and their interpretations mау bесоmе precedents for other courts. “he doctrine of precedent is а central feature of modern соmmоn law system.
“here exist two big areas of law: the Criminal Law area and the Civil Law area. There is а common distinction between them. Criminal law is concerned with antisocial acts of individuals. It is to maintain реасе and order in а society. Civil law is the part of law that defines and determines the rights of individuals, their duties and obligations towards one another. It is established tо protect person and property.
V. Do the following exercises:
Exercise 1. Read and translate the following words into English:
custom, government-made rule, court rulings, to prescribe, Roman law, English Common Law, codified legal system, to influence the law, precedent, area of law, Criminal law, Civil law, to maintain реасе and order, obligation, to establish.
Exercise 2. Translate the following word combinations into English:
иметь отношение (к), ограничение (на), предписанное право, общественные организации, система права, попытки правительства, создать р€д правил, главным образом, правительственное законодательство, примен€ть право, создавать законы, основна€ черта, различие, права человека, защищать личность и собственность, становитьс€ прецедентом.
Exercise 3. Look through the text. Find sentences to prove the following statements:
1. Law as а complex social phenomenon.
2. Prescriptive laws.
3. Two main systems of law.
4. Two main areas of law.
Exercise 4. Speak about law, using exercise 3 as a plan.
V. Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
PENAL LAW
In our country a person is criminally responsible at the age of 16 as a rule, and at the age of 14 if he committed a grave crime. CriminalЕ The basic punishments in our country are: deprivation of liberty, fine,Е Deprivation of liberty is applied for a period of time from 6 months up to 30 years. Adult offenders serve theirЕExercise 1. Find pairs of synonyms.
crime, liberty offender, accordance. inmate, punishment, to release, freedom, to use, conformity, basic, term, youthful, to discharge, juvenile, penalty, criminal, serious, fundamental, grave, to apply, period, offence,prisoner,
Exercise 2. Find pairs of antonyms.
to discharge, juvenile, innocent, to deprive, to help, guil≠tyбspecial, to prevent, criminal; adult, conditional, military, unconditional, before, law-abiding, ordinary, civil, after.
Exercise 3. Match English and Russian equivalents.
2. штраф¬. arrest 3. исправительные работы C. compulsory labour 4. об€зательные работы D. restriction of libertyExercise 4. Complete the sentences.
2. It is applied in relation to persons Е committing a crime. 3. It is also a measure for ... . 4. The purposes of criminal punishment are: to punish con≠victed Е , to reform Е , and to help thembecome ЕЕExercise 5. Speak about Penal Law using the plan.
2. Purposes of punishment. 3. The age of criminal responsibility in Russia. 4. The organ imposing a criminal punishment.PENAL REFORMERS
John Howard is the most famous among penal reformers. He devoted all his life to the problems of improving bad conditions in prisons. He wrote theЕ Benjamin Rush and Alexander Maconochie paid much attention to the punishmentЕ Thanks to John Augustus a concept of probation was born.Exercise 1. Read the names.
Exercise 2. Read and translate the chains of words into Russian: penal Ц to penalize Ц penologist Ц penalty; crime Ц criminal; to contribute ЦЕExercise 5. Fill in the gaps if it is necessary. Translate the sentences.
1. John Howard is the most famous Е penal reformers.
2. He devoted his life Е the problems Е improving bad conditions Е prisons.
3. The book ЂThe State of Prisonsї influenced Е the penal reform of Е Europe.
4. Benjamin Rush paid much attention Е the punishment Е criminals.
5. John Howard made a great contribution Е the penal reform Е Europe.
6. Thanks ... John Augustus the concept ... probation was born.
Exercise 6. Open the brackets. Translate the sentences.
2. Famous penologists (to make) a great contribution to reforming prison system. 3. Zebulon Brockway (to introduce) the idea of education and training forЕ 4. HowardТs book (to influence) the penal reform in Europe and the USA.Exercise 7. Answer the questions.
2. Did they make great contribution to reforming prison system? 3. Who is the most famous among penal reformers? 4. What did John Howard devote his life to?JOЌN HOWARD
In the history of the modern world many реорlе made а great contribution to reforming the prison system in their own countries. We know such namesЕ John Howard is the mоst fаmous among реnаl reformers. Ќе was born in 1726. InЕ In 1773 he bесаmе а sheriff of Bedfordshire. Ќе saw mаnу abuses in penal institutions аnd attacked them. Thanks toЕExercise 2. Fill in the gaps. Translate the sentences.
1. Famous penologists made а great contribution to ... .
2. Howard and other passengers were incarcerated in ... .
3. ќn his return to England Howard secured ... .
4. This incarceration influenced ... .
5. Ќе attacked ... .
6. The bills drafted bу Howard corrected ... and improved ... .
7. HowardТs book aroused ... .
8. The Penitentiary Act of 1779 provided for ... .
Exercise 3. Read the text. Render it in English.
—ейчас целью испpавительныx учреждений €вл€етс€ не только наказание преступников, но и их исправление. ћного внимани€ также удел€етс€ санитарнымЕ –аньше преступники содержались в очень плохих услови€х. ¬ наши дни в местахЕ ¬ наши дни реформы уголовно-исполнительной системы вызывают живой интерес в обществе.ALTERNATIVES TO PRISONS
The basic alternatives to custody in our country are: verbal sanctions, such as admonition, reprimand and warning; fine; compulsory labour;Е In many countries probation, verbal sanctions, financial penalties of someЕExercise 6. Read the following sentences. Translate them into Russian.
2. The most familiar power of this kind is that of disqualifying an offender from driving a motor vehicle or from holding a driverТs license. 3. Other forms of disqualification may be imposed on offenders convicted ofЕExercise 7. Speak about alternatives to prisons.
IV. Read and translate the text with a dictionary:
ALTERNATIVES TO CUSTODY
The basic alternatives to custody in our country are: verbal sanctions, such as admonition, reprimand and warning; fine; compulsory labour;Е In many countries, verbal sanctions, financial penalties of some sort, orЕ Probation began in 1841 when a cobbler named JohnAugustus requested that judges let him pay fines for and superviseЕExercise 4. Speak about alternatives to custody.
THE PROFESSION OF PSYCHOLOGIST I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: at present Ц в насто€щее врем€THE PROFESSION OF A PSYCHOLOGIST
Psychologists study the behaviour of participants in the criminal trial, problems of criminal behaviour, the motives for the crime. A goodЕ III. Do the following exercises:Exercise 8. Fill in the blanks with prepositions where necessary. Translate the sentences.
Exercise 9. Check up your understanding of the text. Fill in the blanks with the proper words: 1.The development of corrections depends on the Е of psychologist. 2. TheЕPSYCHOLOGICAL SCHOOLS
It is the field of study which seeks to describe , understand, predict and control the behaviour of living organisms. The word psychology means theЕ Structuralists, led by Wilhelm Wundt, saw psychology as the study of consciousЕ Another group of psychologists , known as the functionalists, defined psychology as the study of manТs adjustment toЕExercise 8. Make up a plan to the text and speak about psychology as a separate science.
I. Read the and learn the following words and phrases: contemporary Ц современный ramified Ц разветвленныйJURIDICAL PSYCHOLOGY
Forensic psychology investigates the psychological peculiarities of the behaviour of the participants of the trial, psychological aspects ofЕ Corrective psychology deals with rehabilitation of law-breakers inЕ Corrective psychology investigates the psychological problems of reformation through conviction and compulsion.THE GREAT PSYCHOLOGIST.
Wilhelm Wundt was born in 1832 in Baden. He got a degree in medicine, but turned to psychology in his early post-graduate research. WundtТs knowledge was encyclopedical. He wrote not only on psychology , butЕ The largest part of his work was devoted to the senses, especially to vision. He also studied attention, emotionalЕExercise 5. Find in the text all the instances of Passive constructions and give their best possible translations.
1. Ёти процессы называютс€ ассоциативными. 2. ¬ 1879 году была открыта перва€ психологическа€ лаборатори€. 3. нига посв€щена проблемам современной психологии.II. Read the text.
Any attempt to understand human behaviour psychologically involves the study of personality. Research in the field of personality is difficultЕ The Greek physician Galen began to take interest this problem. He suggestedЕ The famous German philosopher Immanuel Kant advocated GalenТs system and also held this view. However this typology isЕTHE BASIC TYPES OF RELATIONS
Psychology seeks to fully understand human behavior. So it must study man in relation not only to himself but also to other individuals, groups ofЕ Person-to person relationships is the simplest form of social interaction.TheЕ Person-to-group relationships. We all belong to various groups, clubs, political groups which form the structure ofЕExercise 4. Give short characteristics of each type of human relationships.
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCHOOLS I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: to appear Ц показыватьс€, по€вл€тьс€PSYCHOLOGICAL SCHOOLS
It is the field of study which seeks to describe , understand, predict and control the behaviour of living organisms. The word psychology means theЕ Structuralists, led by Wilhelm Wundt, saw psychology as the study of consciousЕ Another group of psychologists , known as the functionalists, defined psychology as the study of manТs adjustment toЕExercise 8. Make up a plan to the text and speak about psychology as a separate science.
SOCIAL WORK IN PENAL INSTITUTIONS I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: to root Ц пускать корниSOCIAL WORK IN PENAL INSTITUTIONS
Modern social workers takes part in solving the diversified problems of different levels. There is a particular place for professional social work in prisons. TheЕ The social worker has an obvious role in giving immediate and Уfirst aidФ help. Offenders coming to custody have manyЕFind in the text as many international words as possible and translate them.
the practice Е rendering assistance; to take part Е solving problems; problems Е different levels; a place Е social worker; to adjust Е prisonЕ 3. Make up logical word combinations and translate them into Russian: to be developed obligationsTRAINING OF CORRECTIONAL STAFF IN GREAT BRITAIN.
PSYCHOLOGISTS AND SOCIAL WORKERS IN PRISON SERVICE
With regard to psychologists and social workers the prison service is the biggest single employer of psychologists in Great Britain. There are moreЕ WHAT DO PSYCHOLOGISTS DO IN PRISONS? The psychology service has had difficulty in finding the proper role. The original reason why psychologists wereЕExercise 1. Read the international words and guess their meaning.
business market bank
firm product company
organization to finance basic
production operation corporation
personal management partner
capital to form to combine
license group privilege
limited authority idea
Exercise 2. Match English and Russian equivalents.
долги и убытки 2. to manage a sales force b. частное владение 3. proprietorship c. владелец акцийExercise 3. Choose the right word or word-combination.
a) partnership b) proprietorship c) corporation 2. The proprietor is responsible for all personal and business ЕЕ . a) debts and losses b) banks c) insurance companiesExercise 4. Complete the sentences.
1. To finance the operation business firms deal with ЕЕ .
2. There are three basic kinds of business firms ЕЕ .
3. A proprietorship is ЕЕ .
4. Among disadvantages of proprietorship the following are worth mentioning ЕЕ .
5. Advantages of the proprietorship may be ЕЕ .
6. Disadvantages of corporation may be as follows ЕЕ .
Exercise 5. Insert the necessary prepositions.
1. Business firms are organizations that are engaged Е production.
2. To finance their operations business firms deal Е banks and insurance companies.
3. The proprietor is responsible Е all personal debts and losses.
4. The owner should obtain a license required Е the law.
5. Partnerships are based Е agreement.
6. Corporation is an entity formed and owned Е a group Е people.
Exercise 6. Mark the sentences that are true.
2. There are three basic kinds of business firms: proprietorships, partnerships, corporations. 3. The proprietorship has several advantages such as variety of skills,Е 4. Corporations are firms owned jointly by two ore more persons who are co-owners of business for profit.Exercise 7. Answer the questions on the text.
1. How many legal forms are available to small firms?
2. What are the legal requirements for starting a business as a proprietorship?
3. What is a partnership agreement? What does it include?
4. What is the corporation?
5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of legal form of small business: a) proprietorship; b) partnership; c) corporation?
Exercise 8. Speak about the types of business firms.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: enterprise Ц организаци€ valuables Ц ценностиB A N K S A N D B A N K I N G
Banks are different in different countries. There are many kinds of banks: commercial, saving, national, export Ц import banks and others. MajorЕ Banks provide a wide range of financial services and different types ofЕ If you want to have some interest on the money in the bank you should use saving accounts. Then the customer is givenЕExercise 1. Memorize the following pairs of derivatives.
N Ц Adj
commerce Ц commercial profit Ц profitable
nation Ц national grade Ц gradual
person Ц personal center Ц central
V Ц N
to provide Ц provision to organize Ц organization
to cooperate Ц cooperation to establish Ц establishment
to add Ц addition to operate Ц operation
Exercise 2. Read and translate the given word combinations from English into Russian.
Banking activity; the major source; gradually evolved; to cooperate with each other; to receive and hold deposits; to lend money at interest; to move money from one place to another; to earn profits; to provide financial services; to pay for expenses; to record banking operations; to issue banknotes; to give a passbook; to finance imports and exports.
Exercise 3. Translate the word combinations from Russian into English.
—берегательна€ книжка; личные расходы; предлагать клиентам различные виды счетов; получать процент от денег; фиксировать банковские операции; основной источник дохода банка; широкий спектр финансовых услуг; личный счет; сберегательный счет; сотрудничать друг с другом.
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences.
1. Modern banks gradually evolved from Е Е Е .
2. Banks are commercial enterprises that Е Е Е .
3. Modern banks provide a Е. Е Е of financial services.
4. Е Е Е are used by individuals who wish to earn interest on the money in the bank.
5. The customer is given a passbook in which Е Е Е .
6. Е Е Е is the most profitable banking activity.
7. Major commercial banks in great cities Е Е Е.
Exercise 5. Insert the necessary prepositions.
2. Commercial banks seek to earn profits Е their owners. 3. Modern banks offer their customers different types Е accounts. 4. Personal chequing accounts are used Е individuals to pay Е their expences.Exercise 6. Answer the questions on the text.
2. What is the oldest and the most important banking function? 3. What is the most profitable banking activity? 4. What services do modern banks provide?Exercise 7. Speak about banks and their functions.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: agency Ц орган responsible Ц ответственныйMY FUTURE PROFESSION
After graduating from the Academy many of us will work at correctional institutions as production foremen, sales managers, inventory managers,Е Managing the time of prisoners is one of the major problems of institutionalЕ Work programs known as prison industry has been utilized to meet a variety of goals:Exercise 1. Find and read the international words from the text. Guess their meaning.
Exercise 2. Translate the following derivatives:
economy Ц economist Ц economics Ц economical Ц economically Ц to economize; special Ц specialist Ц specialization; to correct Ц correction Ц correctional; finance Ц financial; to account Ц account Ц accountant Ц accounting; to manage Ц manager Ц management; to know Ц knowledge; to investigate Ц investigator Ц investigation; to tax Ц tax Ц taxation; to produce Ц producer Ц product Ц production.
Exercise 3. Translate the word combinations from English into Russian.
Exercise 4. Match English and Russian equivalents.
1) inventory check a) налогова€ инспекци€
2) taxation agency b) мастер производства
3) audit check c) ревизи€ товарно-материальных ценностей
4) production foreman d) производственный план
5) sales manager e) зав. отделом сбыта
6) inventory manager f) зав. отделом мат.-тех. снабжени€
7) production plan g) аудиторска€ ревизи€ (проверка)
Exercise 5. Make up correct word combinations.
to detect reports financial crimes
to know crimes correctional reports
to make up knowledge perfect institutions
to get specialists responsible knowledge
 to train laws and principles economic job
to train laws and principles economic job
Exercise 6. Insert prepositions where necessary.
2. The work Е an economist is very responsible. 3. Our Academy trains workers Е correctional institutions. 4. After graduation Е the Academy weТll be able to work Е the Economic Crimes Investigation Departments.Exercise 7. Complete the sentences.
2. We also must get Е Е Е Е . 3. We are taught to Е Е Е Е Е Е , Е Е Е Е Е . 4. After graduating from the Academy we can work at Е Е Е or ЕExercise 8. Answer the questions on the text.
2. Where can you work after graduating from the Academy? 3. What duties can the economists at the corrections perform ? 4. What important things are you taught?Exercise 9. Speak about your future profession.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: resources Ц ресурсы land Ц земл€TYPES OF ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
There are a number of ways in which a government can organize its economy.
An economic system is the way in which a country uses its available resources (land, workers, natural resources, machinery, etc.) to satisfy the demand of its inhabitants for goods and services.
There are three main economic systems.
Planned economies.
The state decides what the nation will produce. It usually plans five years ahead. Planned economies have a number of advantages: - everyone in society receives enough goods and services for a basic standard of living;Market economies.
In a true market economy the government plays no role in the management of the economy. The system is based on private enterprise with private ownership of the means of production.
In a market economy the decisions of many individual buyers and sellers interact and determine the answers to the questions: whatto produce, howto produce and whowill receive these goods? Resources in a market economy are allocated with the laws of supply and demand.
Mixed economies.
There are no pure market economies in the world today. Many countries have mixed economies in which private enterprise and government sector exist side by side.
The aim of mixed economies is to avoid the disadvantages of both systems and enjoy the benefits that they both offer.
III. Do the following exercises:
Exercise 1. Read and translate the given derivatives.
to produce Ц production Ц productive
to govern Ц government Ц governmental
to organize Ц organization Ц organized
to satisfy Ц satisfaction Ц satisfactory
to plan Ц planning Ц planned
to decide Ц decision
to exist Ц existence
to predict Ц prediction
to manage Ц management
to interact Ц interaction
to determine Ц determination
to mix Ц mixture
Exercise 2. Translate the given word combinations from English into Russian.
Exercise 3. Make up correct word combinations.
to organize resources central features
to satisfy disadvantages available enterprise
to divert demand private resources
to receive goods common amount
to avoid economy large planning
Exercise 4. Insert prepositions where necessary.
2. In planned economies everyone ... society receives enough goods and services ... a basic standard ... living. 3. In command economies any profits are paid ... the government. 4. A true market economy is based ... private enterprise ... private ownership ... the means ... production.Exercise 5. Complete the sentences.
2. Planned economies are sometimes called ... ... ... . 3. What the nation will produce usually planned ... ... ... . 4. Command economies have a number of ... and ... .A) translate the sentences which are true;
B) correct the sentences if they are false.
2. Planned economies are sometimes called free enterprise economies. 3. In a true market economy the government takes all the decisions. 4. Market economy is based on private enterprise with private ownership of the means of production.Exercise 7. Answer the questions.
2. How many kinds of economic systems are there in the world today? What are they? 3. Planned economies are economies with a large amount of central planningЕ 4. Who decides production and consumption in command economy?Exercise 8. Speak about basic types of economic systems in the world.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: manufacture Ц производство manufactured goods Ц промышленные товарыExercise 1. Find and read the international words from the text. Guess their meaning.
nature, profitable, industry, independent, exporter, manufactured, natural, natural, unprofitable, growth, dependant, consumer, profit, industrial,Е Exercise 3. Translate the given word combinations from English into Russian:Exercise 4. Match English and Russian equivalents.
manufacture and trade частное предпринимательство
to be rich in forests природные богатства
natural resources на душу населени€
woolen and leather commodities международна€ торговл€
skilled labour промышленность и торговл€
international trade быть богатым лесами
private enterprise шерст€ные и кожаные товары
per head of population квалифицированный труд
Exercise 5. Finish the sentences choosing the right variant.
2. Britain used to be rich in ( natural resources / forests / room for cultivation ). 3. Before World War II British colonies used to supply it with ( precisionЕ 4. Most of BritainТs population is employed in ( manufacturing, building, and mining / agriculture / sheep and cattleЕExercise 6. Open the brackets using the verbs in a proper form (active or passive voice).
2. Britain (to be) one of the largest exporters of manufactured goods per head of population. 3. Most of the forests in Great Britain (to cut down). 4. Most of British people (to employ) in mining, manufacturing and building.Exercise 8. Speak about British economy.
T H E G R E A T E C O N O M I S T I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: science Ц наукаG R E A T E C O N O M I S T S
He was born in 1723 in a small fishing town near Edinburgh, Scotland. At the age of 28 Adam Smith became a Professor of Logic at the University ofЕ With the financial security of his grant Smith devoted 10 years to writing his work which founded economic science.ЕExercise 1. Read and translate the given derivatives.
science Ц scientist Ц scientific to found Ц founder
economy Ц economist Ц economical to appoint Ц appointment
academy Ц academic to compete Ц competitive
theory Ц theoretical to accept Ц acceptable
wealth Ц wealthy to develop Ц development
policy Ц political to consume Ц consumption
finance Ц financial to explain Ц explanation
Exercise 2. Translate the given word combinations from English into Russian.
A great scientist; extraordinary contributions; academic appointment; with the financial security; grant; to devote; lifetime; with great success; the founder of economics; according to; wealth; the competitive nature; to argue; the individual pursuit of self-interest; certain cannons of taxation; generally acceptable; to explain; to benefit; the theory of overpopulation; to put forward the idea; the worst excesses; business cycle.
Exercise 3. Make up suitable word combinations and translate them into Russian.
to emphasize great contributions
to lay competitive nature
to make nature
great success
industrial scientist
basic principle
famous society
competitive basic principles
Exercise 4. Finish the sentences using the right variant. Translate the sentences into Russian.
2. He founded ... 3. At the age of 28 Adam Smith became ... 4. With the financial security of his grant Smith ...Exercise 5. Translate the words and word combinations from Russian into English.
»сследование; согласно (чему-либо); подчеркивать (удел€ть большое внимание); финансова€ поддержка; благососто€ние наций; конкурентный характер; лична€ заинтересованность; общеприн€тый; максимальное общественное благо.
Exercise 6. Insert prepositions where necessary.
1. At the age ... 28 Adam Smith became a Professor ... Logic ... the Glasgow University.
2. Adam Smith devoted 10 years ... writing his book.
3. Smith emphasized the competitive nature ... the industrial society.
4. A. Smith laid the basic principles ... the system ... taxation.
5. T.R. Malthus was an English ... economist ... Classical School.
Exercise 7. Answer the questions.
2. When and where was he born? 3. What was his first academic appointment? 4. What work did he devote 10 years of his life?Exercise 8. Speak about the great economists.
I. Read and learn the following words and phrases: economics Ц экономика (как наука) economic laws Ц экономические законыTHE SCIENCE OF ECONOMICS
Economics is defined as the study of mankind in the everyday business of life. It is a social science. Economics studies our everyday lives and theЕ Everyday business of providing the means of life is called by the general termЕ Economics is the study of economies. It includes a vast range of subjects.Exercise 1. Read the international words and guess their meaning.
Business community system
Economics economy economic
Term management factors
Resources inflation national
Capital regulation nation
Exercise 2. Translate the word combinations from English into Russian.
A social science; economic laws; to affect the prices, wages and earnings; values of output, unemployment and inflation; individual produces; the everyday business of life; to provide the means of life; use and control of the money; a vast range of subjects; to allocate capital; valuable commodities; to make predictions; the essence of economics.
Exercise 3. Translate the given word combinations from Russian into English.
ƒелитьс€ на; микроэкономика и макроэкономика; отдельные производители, потребители и рынки; народное хоз€йство; ведение домашнего хоз€йства; исследовать экономические законы; подъемы и спады в экономике; распределение дохода; поведение финансовых рынков; модели торговли между государствами.
Exercise 4. Choose the right word or word-combination.
a) industry b) mankind c) income 2. Economics studies the general life of our communities in order toЕ a) how to use money b) the behaviour of the financial markets c) the economic lawsExercise 5. Insert the necessary prepositions.
2. Economics studies our everyday lives and the general life ... our communities ... order to understand the whole economic system, to find economicЕ 3. It is the system ... the management, use and control ... the money, goodsЕ 4. Economics as a science consists ... microeconomics and macroeconomics.Exercise 6. Mark the sentences that are true.
2. Economics is a social science. 3. Everyday business of providing the means of life is called by the generalЕ 4. Microeconomics explores the behaviour of the financial markets and analyses how they allocate capital.Exercise 7. Answer the questions on the text.
1. What is the origin of the modern word СeconomicsТ?
2. Is economics a social science?
3. What is called by the general term УeconomyФ?
4. What subjects does economics study?
5. Economists divide economics into microeconomics and macroeconomics, donТt they?
6. What does microeconomics attempt to understand?
7. Does macroeconomics study economy as a whole?
8. What is the essence of economics?
Exercise VIII. Speak about economics science.
THE PROFESSION OF AN ECONOMIST I. Learn the given words and word combinations:M Y F U T U R E P R O F E S S I O N
An economist should have a thorough training in economic theory, mathematics and statistics and our Academy offers such training. At the Academy weЕ An economist needs some knowledge of the world outside his own country becauseЕ The profession of an economist is quite diversified. The graduates of our department work at educational institutions,ЕExercise 8. Be ready to speak about your future profession.
—ќƒ≈–∆јЌ»≈
| ќбщефакультетские устные темы About Myself and My FamilyЕЕ.................................................... Our Academy .................................................................................... Moscow ............................................................................................. Great Britain ...................................................................................... ”стные темы юридического факультета The Russian Federation State System ............................................... The State Structure of Great Britain .................................................. The English Judicial System ............................................................. The Profession of a Penal Officer ..................................................... The Profession of a Lawyer ............................................................... The Law ............................................................................................. Famous Penologists ........................................................................... Alternatives to PrisonsЕЕЕЕ........................................................ ”стные темы психологического факультета The Profession of a Psychologist ...................................................... Psychological ScienceЕ..ЕЕЕ...................................................... Juridical Psychology.......................................................................... The Great Psychologist .................................................................... Personality ЕЕЕЕ.. ...................................................................... The Basic Types of Relations ............................................................ Psychological schools ЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ... Social work in penal institutions ЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ... Supplementary TextsЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ.. ”стные темы экономического факультета Types of ProprietorshipЕ.................................................................. Banks and Banking ........................................................................... The Profession of an Economist in Corrections .............................. Economic SystemsЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ. ЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ British Economy ЕЕ....................................................................... The Great EconomistЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ... Economics and EconomyЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ.ЕЕЕЕЕ The profession of an EconomistЕЕЕЕЕЕЕЕ.ЕЕЕЕЕЕ. |