рефераты конспекты курсовые дипломные лекции шпоры
- Раздел Иностранные языки
- /
- Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера.
Реферат Курсовая Конспект
Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера.
Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера. - раздел Иностранные языки, Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности: Учебное пособие / Радовель В. А. — Изд. 3-е. Text 2. Some Features Of A Digital Computer ...
Text 2. SOME FEATURES OF A DIGITAL COMPUTER
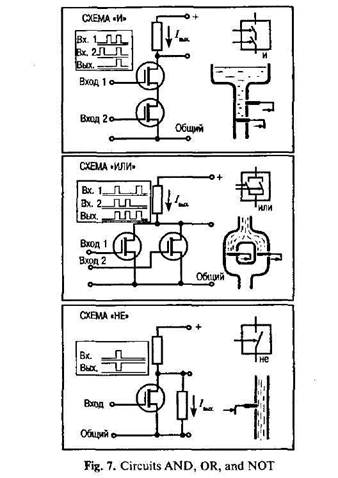
It should be noticed that even in a large-scale digital system, such as in a computer, or in a data-processing, control or digital-communication system, there are only a few basic operations which must be performed. These operations may be operated many times. The four circuits most commonly employed in such systems are known as the OR, AND, NOT and FLIP-FLOP.They are called logic gates or circuits.
An electronic digital computer is a system which processes and stores very large amount of data and which solves scientific
problems of numerical computations of such complexity and with such speed that solution by human calculation is not feasible. So the computer as a system can perform numerical computations and follow instructions with extreme speed but it cannot program itself.
\fe know that the numbers and the instructions which form the program, the computer is to follow, are stored in an essential part of the computer called the memory. The second important unit of the computer is the control whose function is to interpret orders. The control must convert the command into an appropriate set of voltages to operate switches and carry out the instructions conveyed by the order. The third basic element of a computer is the arithmetic device, which contains the circuits performing the arithmetic computations: addition, subtraction, etc. The control and arithmetic components are called the central processor. Finally a computer requires appropriate input-output devices for inserting numbers and orders into the memory and for reading the final result.
Suppose a command to perform an addition or division has been transmitted to the central processor. In response to this order the control must select the correct operands from the memory, transmit them to the arithmetic unit and return to the
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 78
memory the result of the computation. The memory serves for storing not only the original input data, but also the partial results which will have to be used again as the computation proceeds.
Lastly, if the computation doesn't stop with the execution of this instruction and the storage of the partial result, the control unit must automatically pass on to the next instruction. The connection of the control unit back to the input permits insertion of more data when there is room in the memory.
79___________ Unit & Functional Organization of the Computer
10. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис
пользуя информациютекста.
1. What are the most commonly used circuits in any computer? 2. How are they called? 3. What kind of a system is a digital computer? 4. Is there anything that a computer cannot do itself? What is it? 5. Where are the instructions and digits stored? 6. What is the function of the control? 7. What does the arithmetic device serve for? 8. What components form the central processor? 9. What other devices in addition to the above-mentioned ones does a computer require? 10. How are computations performed in a computer?
11. Найдите в тексте английские эквивалентыследующих
сочетаний:
Крупномасштабная цифровая система; система обработки данных; система цифровой связи; наиболее широко распространенные схемы; логические схемы; решать научные проблемы; выполнять числовые вычисления; интерпретировать команды; приводить в действие переключатели; выполнять команды; нуждаться (требовать) в необходимом устройстве ввода-вывода; введение чисел и команд; считывание конечных результатов; передавать команду в центральный процессор; в ответ на; хранение частичных результатов; позволить введение новых данных; свободное место в памяти.
12. Подберите пары или группы близких по значению слов из
предложенных ниже. Переведите слова на русскийязык.
ferbs: relate, employ, insert, perform, remove, operate, show, interpret, select, issue, use, receive, perform, cause, print, make, compute, connect, execute, take away, require, act, convert, carry out, demand, permit, demonstrate, choose, transmit, type, store, get, calculate, proceed, continue, keep, allow.
Nouns:response, unit, component, computation, storage, gate, amount, digit, element, memory, instruction, device, equipment, connection, circuit, order, command, information, relation, quantity, answer, calculation, number, data.
Adjectives:broad, complete, each, appropriate, every, basic, essential, digital, original, full, wide, initial, major, large, numerical, common, necessary, usual, important, general, great.

|
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 80
 13. Согласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретаци
13. Согласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретаци
ей, предложенной справа.
1. Functional organization a) processes and stores large
of a computer amount of data and solves
problems of numerical computations;
2. Input b) circuits used in large-scale
digital systems;
3. Memory c) method of interrelation of the
main units of a computer
4. Control unit d) removing data from the de-
vice to the outside world;
5. Output e) inserting information into
the computer;
6. Arithmetic unit f) a code of combinations of
electric pulses;
7. Machine language g) performs addition, subtrac-
tion, multiplication, etc;
8. Logic gates h) stores original data as well as
partial results;
9. Digital computer i) causes all parts of the com-
puter to act as a team.
14. Расскажите о действии функциональных устройств
компьютера, пользуясь приведенной ниже схемой.
Central processing unit
81 Unit 6. Functional Organization of the Computer
 15. Составьте аннотации на русском языке к следующим текстам по вариантам, используйте упр. 14 на с. 52.
15. Составьте аннотации на русском языке к следующим текстам по вариантам, используйте упр. 14 на с. 52.
1. Logical circuit elements
As it is known, any digital calculation — whether it is performed by 'pencil and paper' methods or with the aid of an automatic computer— must first be broken down into a sequence of elementary arithmetical operations, such as addition, or multiplication. Each such arithmetical operation may be converted into a sequence of simple logical operations. It should be noted that a binary digit may take only two values — "zero" and "one". A logical proposition may be either true or false.
A symbolism and a set of rules suitable for manipulating 'yes or no' logical propositions was developed by George Boole, a self-educated genius who became Professor of Mathematics at Cork University in the middle of the 19lh century. The techniques of Boolean algebra are now extensively used by electrical engineers for the design and analysis of switching circuits. Both the arithmetic and control units of a computer consist of sets of switching circuits for directing and manipulating electrical pulse signals.
The process of combining a number of electronic circuits of known logical properties into an integrated system capable of performing special arithmetical or control functions is known as logical design.
2. The definition of mechanical brain
Let's imagine a railroad line with four stations marked input, storage, computer and output. These stations are joined by little gates or switches to the main railroad line. We can imagine that numbers and other information move along this railroad line, loaded (погруженные) in cars. Input and output are stations where numbers or other information go in and come out respectively. Storage is a station where there are many platforms and where information can be stored. The computer is a special station, somewhat like a factory. When two numbers are loaded on platforms 1 and 2 of this station and the command is loaded on platform 3, then another number is produced on platform^
There is a tower, marked control.This tower runs a telegraph line to each of its little watchmen standing by the gates. The

|
| Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 82 |
tower tells them when to open and when to shut which gates. Now we can see that as soon as the right gates are shut, cars loaded with information can move between stations. So by closing the right gates, we can flash (отражать) numbers and information through the system and perform operations of reasoning. Thus we receive a mechanical brain.
In general, a mechanical brain is made up of: a quantity of registers where information can be stored; channels along which information can be sent; mechanisms that carry out arithmetic and logical operations; a control, which guides the machine to perform a sequence of operations; input and output devices, where information can go into and out of the machine; and at last electricity, which provides energy.
16. Поменяйтесь вариантами и выполните письменный перевод текстов, приведенных выше.
TESTS
1. Подберите вместо пропусков подходящие по смыслу слова.
I. The method of_______ all functional categories to one
another represents the functional organization of a computer, a) showing; b) relating; c) performing
83 Unit 6. Functional Organization of the Computer
 2. Instructions and data are fed through the_____ equip-
2. Instructions and data are fed through the_____ equip-
ment to the_______ .
a) output; b) memory; c) input; d) control
3. The main units of the computer communicate with each
other_______ a machine language.
a) in spite of; b) because of; c) by means of
4. The input also______ the information into the pulse —
no-pulse combinations understandable to the computer, a) converts; b) removes; c) accomplishes
5. The four_______ are used to perform basic operations
in a computer.
a) basics; b) circuits; c) equipment
6. A computer can solve very complex numerical____ .
a) communication; b) computations; c) instructions
7. Numbers and instructions forming the program are
in the memory.
a) solved; b) stored; c) simulated
8. The control unit serves for______ orders.
a) reading; b) interpreting; c) inputting
9. The function of memory is to store_______ the origi-
nal input data_______ the partial results.
a) not only ... but also; b) either ... or; c) no sooner ... than
10. The includes the control and arithmetic-logi
cal units.
a) flip-flop; b) digital computer; c) central processor
2. Заполните пропуски, выбрав правильную грамматическую форму.
1. The simplest digital device is any device which [a) can;
b) could; c) must] count.
2. In ancient days man [a) learns; b) learned; c) has learned]
to substitute beads for fingers to help him count.
3. The ancient Chinese simplified the [a) counted; b) to
count; c) counting] board into abacus.
4. The Japanese improved the abacus making it [a)more ef
ficient; b)much efficient; c) efficienter].
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 84
5.  The tremendous speeds of computers and the flexibility
The tremendous speeds of computers and the flexibility
[a) building; b) built; c) to build] into them [a) because
of; b) according to; c) due to] the logical control make
modern computers more powerful than mechanical cal
culators.
6. The big problem in understanding digital computers is the
logic which relates the logical elements into a unit [a)
performed; b) performing; c) having performed] arith
metic and logical operations.
7. Arithmetic operations [a) converted; b) are converted;
c) was converted] into a sequence of simple logical oper
ations.
8. Any digital calculation is usually [a) breaking; b) broken;
c) being broken] down into a sequence of elementary
operations.
9. A computer is a device [a) to accept; b) has accepted;
c) accepts] a set of instructions and [a) executes; b) exe
cuted; c) to execute] them in the appropriate sequence.
lO.The flip-flop [a) is; b) was; c) has been] a storage cell with two inputs and two outputs.
Unit 7 STORAGE
 1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
primary / secondary storage — первичное / вторичное запоминающее устройство
main storage — основная память; оперативное запоминающее устройство
internal storage [in'tanal] — внутреннее ЗУ sequence ['sikwans] — последовательность; порядок следования
intermediate results [,mte'midrat nsAlts] — промежуточные результаты
ongoing process ['ongoing 'prousss] — продолжающиеся), постоянный процесс
similarity [simi'lseriti] — сходство; подобие to retain [п Чет] — сохранять; удерживать to locate [lou'keit] — размещать(ся); располагать(ся) value ['vaeljir.] — значение, величина; значимость, ценность; оценка binary digit ['Ьатэп 'did^it]— двоичная цифра; двоичный
знак
adjacent [э'йзевэШ] — смежный; соседний; примыкающий
strings of characters — последовательность символов consecutive [ksn'sekjutiv] — последовательный; смежный; соседний
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, что такое запоминающее
устройство в компьютере и о каких еготипах выузна
ли из текста.
Text 1.STORAGE UNITS
Computer system architecture is organized around the primary storage unit because all data and instructions used by the

|
| Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 86 |
computer system must pass through primary storage. Our discussion of computer system units will begin with the functions of the primary and secondary storage units. This leads to the examination of the central processing unit and from there to the consideration of the input and output units. Therefore, the sequence in which we'll describe the functional units of a digital computer is: 1) storage units, primary and secondary; 2) central processing unit; 3) input and output units.
As you know, there are primary and secondary storage units. Both contain data and the instructions for processing the data. Data as well as instructions must flow into and out of primary storage.
Primary storage is also called main storage or internal storage. The specific functions of internal storage are to hold (store): 1) all data to be processed; 2) intermediate results of processing; 3) final results of processing; 4) all the instructions required for ongoing process. Another name for primary storage is memory, because of its similarity to a function of the human brain. However, computer storage differs from human memory in important respects. Computer memory must be able to retain very large numbers of symbol combinations, without forgetting or changing any details. It must be able to locate all its contents quickly upon demand. The combinations of characters, that is, the letters, numbers, and special symbols by which we usually
87 Unit 7. Storage
 communicate, are coded. The codes used by computer designers are based upon a number system that has only two possible values, 0 and 1 .'A number system with only two digits, 0 and I, is called a binary number system. Each binary digit is called a bit, from Binary digiT. As the information capacity of a single bit is limited to 2 alternatives, codes used by computer designers are based upon combinations of bits. These combinations are called binary codes. The most common binary codes are 8-bit codes because an 8-bit code provides for 2/8, or 256 unique combinations of l's ans O's, and this is more than adequate to represent all of the characters by which we communicate.
communicate, are coded. The codes used by computer designers are based upon a number system that has only two possible values, 0 and 1 .'A number system with only two digits, 0 and I, is called a binary number system. Each binary digit is called a bit, from Binary digiT. As the information capacity of a single bit is limited to 2 alternatives, codes used by computer designers are based upon combinations of bits. These combinations are called binary codes. The most common binary codes are 8-bit codes because an 8-bit code provides for 2/8, or 256 unique combinations of l's ans O's, and this is more than adequate to represent all of the characters by which we communicate.
Data in the form of coded characters are stored in adjacent storage locations in main memory in two principal ways : 1) as "strings" of characters — in bytes; and 2) within fixed-size "boxes" — in words. A fixed number of consecutive bits that represent a character is called a byte. The most common byte size is 8-bit byte. Words are usually 1 or more bytes in length.
Secondary storage. Primary storage is expensive because each bit is represented by a high-speed device, such as a semiconductor. A million bytes (that is, 8 million bits) is a large amount of primary storage. Often it is necessary to store many millions, sometimes billions, of bytes of data. Therefore slower, less expensive storage units are available for computer systems. These units are called secondary storage. Data are stored in them in the same binary codes as in main storage and are made available to main storage as needed.
– Конец работы –
Эта тема принадлежит разделу:
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности: Учебное пособие / Радовель В. А. — Изд. 3-е.
Научный консультант... Соколов С В доктор технических наук профессор действительный член... Рецензент Понкратова Ю Г зам директора гимназии г Ростова н Д председатель методобъединения учи телей английского языка...
Если Вам нужно дополнительный материал на эту тему, или Вы не нашли то, что искали, рекомендуем воспользоваться поиском по нашей базе работ: Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера.
Что будем делать с полученным материалом:
Если этот материал оказался полезным ля Вас, Вы можете сохранить его на свою страничку в социальных сетях:
| Твитнуть |
Хотите получать на электронную почту самые свежие новости?







Новости и инфо для студентов