рефераты конспекты курсовые дипломные лекции шпоры
- Раздел Иностранные языки
- /
- З дисципліни Іноземна мова англійська
Реферат Курсовая Конспект
З дисципліни Іноземна мова англійська
З дисципліни Іноземна мова англійська - раздел Иностранные языки, Міністерство Освіти І Науки України Херсонський Нац...
МІНІСТЕРСТВО ОСВІТИ І НАУКИ УКРАЇНИ
ХЕРСОНСЬКИЙ НАЦІОНАЛЬНИЙ ТЕХНІЧНИЙ УНІВЕРСИТЕТ
Кафедра іноземних мов
Рег. № 64/310 – 02.04.09
методичні рекомендації
до практичних занять
з дисципліни Іноземна мова (англійська)
для студентів 1 курсу
для напряму підготовки всіх напрямів підготовки
галузі знань всіх галузей знань
факультету всіх факультетів
Херсон – 2009р.
Методичні рекомендації до практичних занять з дисципліни іноземна мова (англійська) для студентів 1 курсу всіх напрямів підготовки всіх галузей знань всіх факультетів.
Укладач (і): Фоменко Н.С., Головіна О.О., ГрицинаЛ.В., Голованова Н.П. кількість сторінок 170 .
Рецензент: доц. Смирнова Н.В
Затверджено
на засіданні кафедри іноземних мов
протокол № _7_ від __2.03.09____
Зав. кафедри доц.Фоменко Н.С.
Відповідальний за випуск Н.С.Фоменко к.філол.н., доц., завідувач кафедри іноземних мов
Вступ.
Методичні вказівки являють собою корективний курс для студентів 1 курсу немовних вузів. Завдання корективного курсу полягає в тому щоб відпрацювати на певному лексичному матеріалі основні вміння і навички вживання в усному мовленні нескладних граматичних конструкцій, вміння читати, говорити і сприймати тексти побудовані на тому ж мовному матеріалі.
Оскільки метою корективного курсу є розвиток розмовних навичок в першу чергу, то система лексико-граматичних вправ будується на основі рішення комунікативних завдань.
На певному лексичному матеріалі відбувається навчання всім видам мовної діяльності. Кожному виду мовної діяльності відповідають свої вправи, які відображають його специфіку. Важливим являється створення реальних та уявних ситуацій спілкування, які спонукають до рішення комунікативних завдань (розпитати, повідомити, виразити думку, довести).
До корективного курсу входить короткий фонетичний довідник, представлений у вигляді зведених таблиць і вправи для розвитку вимовних навичок.
|
I. Language
Illustrative Examples
Have you a book? Yes, I have. No, I have not. I have no book. I haven’t any book.Exercise 1. Render the following sentences into the Past and the Future.
1. I have a large family. 2. He has many friends.Exercise 4. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
Use the table. Form interrogative sentences in the Past with “did”. …Exercise 5. Say it in English.
2. У нас немає часу піти туди. 3. Скільки часу ти мав для написання статті? 4. В мене був велосипед.Read and translate the text.
Our Language laboratory.
III. Practice.
1. Ask your fellow student about the University language laboratory.
2. Describe your English classes in the language laboratory.
|
I. Language
Affirmative (стверджувальна форма) Interrogative (питальна) Negative (заперечна) …Illustrative Examples
I am a student. I am not a pupil. I was a pupil last year.Exercise 1. Render the following sentences into the Past and the Future.
2. She is a good student. 3. You are our guests. 4. I am a member of this group.Exercise 3. Answer the following questions.
1. Is your father an engineer?
2. Will you be an economist?
3. Who is the eldest in your family?
4. Are your parents in England?
5. Your mother was a famous dancer, wasn’t she?
6. Who are you?
7. What are you?
8. Is your best friend a student or a collective farmer?
9. Shall we be friends?
10. Where were you yesterday in the evening?
Exercise 4. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
1. Victor Petrov is a student.
2. He is a famous scientist.
3. They were members of our society.
4. My friend is a famous artist.
5. She was a good research worker.
6. I am a student of KSTU.
7. We were good friends.
8. The house of his grandfather is very old.
Exercise 5. Say it in English.
1. Твоя мати була студенткою цього університету?
2. Він відомий науковець, чи не так?
3. Я не учень а студент.
4. Вони Українці.
5. Вoна не на роботі.
6. Мій дідусь був професором в університеті.
7. У майбутньому я буду хорошим спеціалістом.
8. Хто автор цієї статті?
9. Вони були добрими друзями.
10. Твій брат буде завтра на лекції?
II. Reading
Text
My friends
I have many friends. My best friend is Vladimir Petrov. He is a student too. But he is not a student of KNLU. He is a student of Kharkov Pharmacy … Lena Pavlova is my girl friend. She is 18, but she is not a student. She is a… I also have a friend in England. His name is Steven King. Is he Ukrainian? No, he is not. He’s English. Is he a…III. Practice
a) His/her family; b) His/her friends. Get the information about: names, surnames, ages, nationalities, relatives, occupations.Grammar
Construction there + be
The Present Indefinite Tense
The Past Indefinite Tense
Indefinite Pronouns
Illustrative Examples
There are student hostels at the University. Is there a post-graduate course at the University? Yes, there is. No, there is not.II. Language
Exercise 1. Study the vocabulary
competition – конкурс to enter – поступати to do one’s best – робити все можливеIII. Grammar
Exercise 1. Render the following sentences into the Past.
1. There is no library at the University. 2. There is an amateur group at the University.Exercise 4. Express your surprise as in the model. Give short affirmative (negative) answers as in the model.
1. There is a newspaper on the table. 2. There were many parks in the town. 3. There is a Cybernetics faculty on the second floor.Exercise 6. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
1. There are three student hostels at the University. 2. There are seven faculties at the University.Exercise 7. Say it in English.
2. В університеті є бібліотека. 3. Чи є в університеті лабораторії із сучасним обладнанням? 4. Скільки студентських гуртожитків є в університеті?Exercise 8. Make up the sentences. Use the chart.
Exercise 9. Fill in the blanks withsome (something, somebody), any (anybody, anything), no (nothing, nobody).Render the sentences into Ukrainian. … 1. There is … in the class-room. 2. There were … mistakes in the term-paper.IV. Reading
Text A
Read and translate the text A
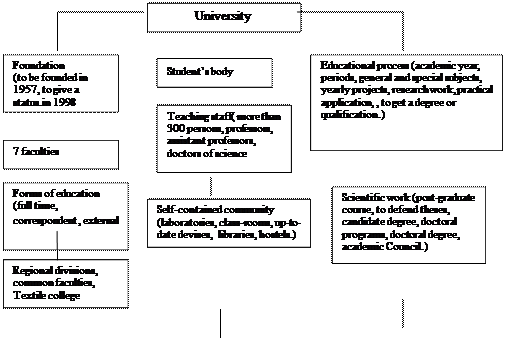
Educational establishment was founded in 1957. In 1980, on its bases the Kherson State Industrial Institute was opened. In 1998 it was given the… About eight thousand students study at the University. The teaching staff is… The students have at their disposal experimental shops, laboratories with modern equipment, language laboratories for…V. Language
- higher educational establishment; - faculty of Mechanical Engineering; - practical application;VI. Comprehension
1. KSTU is one of the best higher educational establishments in Ukraine. 2. Now, there are two buildings and three hostels at the University. 3. About six hundred students study at the University.VII. Practice
Speak on the topic “ My University.”. Use the chart.
 |
VIII. Comprehension
to be situated – бути розташованим entrance exams – вступні іспити to be like somebody (something) – бути схожимText B
Oxford
The city of Oxford is like London. It is old, international and it is situated on the river Thames. Oxford is very beautiful and green city. We say that Oxford is old and historical because it was founded in 912. The University was founded in 1249. Oxford is international because people from many parts of the world come to study at this University. Every year more than one thousand students enter Oxford University. The entrance exams are difficult. It is necessary to work hard to become a student of the Oxford University. Oxford University is residential. It consists of 38 colleges and each student must belong to one of the colleges.
The academic year in England has three terms which usually last from the beginning of October till the middle of December, from the middle of January till the end of March and from the middle of April till the end of June. There are examinations at the end of each term. If a student fail in an exam, he may be allowed pass the exam again. Only two reexaminations are usually allowed.
The University of Oxford has a tutorial system of education: every student has a tutor who plans his work. Each week some students come to see him, they discuss different questions connected with their studies and research work. At Oxford University no student may call on a tutor or attend a lecture without his or her gown, therefore the students wear them in all weather or carry them over arm or shoulder.
The students at Oxford University spend a lot of time studying. Their working hours are from 9 to 1. At 9 o’clock they see the tutor or go to the library or to the lecture. From 2 to 5 they are engaged in sports and all kind of exercises. Almost all students go in for some kind of sport. The most famous kinds of sport are: boxing, running, playing football, golf and other games. From 5 to 7 they usually either work in the library or in the laboratory. At 7 o’clock the undergraduates and tutors gather in the hall and have dinner. After dinner students have club activities, debating societies etc. By 10 o’clock the students must be in the college, as most of the students live in the colleges. At 10 o’clock the students sit down to work again and work about 2 hours. At 12 o’clock p.m. the students go to bed. The life of the students at Oxford is very interesting.
Exercise 1. Find the right ending of the sentences.
a) it is large and beautiful. b) it is old historical and it is on the river Thames. c) many books are written about it.Exercise 2. Agree or disagree with the following statements.
2. The University was founded in 1978. 3. Oxford University consists of 28 colleges. 4. Every year more than one thousand students enter the Oxford University.Exercise 3. Put the following sentences into the right order according to the text.
1. The academic year in England has three terms.
2. It is necessary to work hard to become a student of the Oxford University.
3. The students at Oxford spend much time studying.
4. The city of Oxford is old, international and beautiful.
5. Examinations take place at the end of each term.
6. Every year more than one thousand students enter the Oxford University.
7. The University of Oxford has a tutorial system of education.
IX. Practice
Exercise 1. Compare KSTU with the University of Oxford.
Exercise 2. Read and act the dialogue.
Student B: How do you do A? I’m glad to meet you. My name is B. You see, I’m a first year student too, at Oxford University. St.A: What faculty do you study at? St B: I’m a student of the Slavonic faculty. And you? What faculty do you study at?X. Reading
1. What are the main types of British schools? 2. What is the difference between them? 3. When is secondary education compulsory for children?Exercise 2. Read the words for the text and learn their meaning.
Free of charge – безкоштовно
Infant School – школа для малюків
Junior School – молодша школа
Comprechnsive School – загальноосвітня школа
“GCSE” – свідоцтво про середню освіту
Vocational school – професійно-технічне училище
Advanced level – підвищений рівень
Master degree – ступінь магістра
Text C
The Educational System of Great Britain
In private schools parents pay for education. 7% of children attend them. It is rather difficult to get to the most famous schools such as Eton,… At five all children go to Infant School and stay there till they are seven.… At 11 pupils go to a secondary school called comprehensive. In this school there are different programmes: the Grammar…XII. Reading
Exercise 1. Read Text D and learn more about the educational system of Ukraine. Read the following words to the text and learn their meaning.
Improving qualification courses – курси підвищення кваліфікації
Beyond-the-school education – позашкільна освіта (знання, які набувають школярі, займаючись у гуртках, будинках та палацах школярів тощо).
Doctorate courses – докторантура
Distance learning – дистанційне навчання
Text D
The educational system of Ukraine
In Ukraine the education is compulsory for all children between the age of 6 to 15. Mainly all schoolchildren attend state schools, where education… Pre-school education is provided by kindergartens. Secondary education give a… For adults there are evening and distance learning secondary schools.XIII. Practice
Exercise 1. Tell about the educational system of Ukraine. Use the chart.
Exercise 2. Compare the educational system of Ukraine and Great Britain. What is common? What is different? Use the following plan. 1. Age of compulsory education. 2. Types of schools.Supplementary Reading
Open University
Apart from the well-known degree courses there are a lot of other courses, some lasting only a few weeks, others ten or twelve months. Courses cover a wide range of subjects – from every-day topics though… There are nearly 200 courses and in all of them (except for higher degrees) there is only one principle: they are open…American Educational System
Americans tend to study a larger number of subjects than Europeans, in school, and particularly at the university. Seven subjects are required for a… There are more than two thousand institutions of higher education in the… The first two years in an American college or university differ somewhat from a similar period in a European one.…Students Студенти
to enter — поступати; to graduate (from) — закінчувати вашій учбовий заклад; bright / capable student — здібний студент;Hostel Гуртожиток
group-mate — товариш по групі; recreation hall — зал відпочинку; students’ canteen — їдальня;II. Grammar
The Present Indefinite Tense( Present Simple )
Sentence patterns
Key examples to be memorized
| I study hard. Do you study hard? I don’t study hard. |
Illustrative Examples
Does he attend lectures and seminars? Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t. He doesn’t attend lectures and seminars.Adverbial Modifiers of Time
usually — sometimes always — never every day / — from time to timeThe Past Indefinite Tense (Past Simple )
Sentence Patterns
Illustrative Examples They missed a lecture yesterday . Did they miss a lecture yesterday?Past Indefinite Tense
Adverbial Modifier of time
Exercise 1. Put the verbs given below in the Past Indefinite Tense. Explain the reading of ending – ed([d],[t],[id]) in the regular verbs . Make 2… to become, to do well, to give a lecture, to attend a language laboratory, to…I made up my mind to enter the University.
My friend passed all the exams successfully.
She became a first-year student.
They took satisfactory marks yesterday.
She was good at Physics last week.
Exercise 4. Object to the sentences. Use the phrases: No , it is not so. I am afraid you are wrong. I can’t agree with you. On the contrary as in… He came from the country. —You are wrong. He didn’t come from…Exercise 6. Add tag-questions to the following statements and agree or disagree with them as in the model.
1. a) My niece studied English in the Language Laboratory yesterday .A) It took him 40 minutes to get to the University.
3. a) The students had a good time together b) The students didn’t have a good time together . 4. a) Boris went to a farewell party at his school yesterday .Exercise 9. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
1. The students played football in the afternoon. 2. He received the telegram from their parents on Saturday. 3. We had a get together last week.The Future Indefinite Tense (Future Simple)
Sentence Patterns
Key examples to be memorized:
| The teacher will give a lecture tomorrow. Will the teacher give a lecture tomorrow? The teacher will not (won’t) give a lecture tomorrow. |
Illustrative Example
They will live in the hostel.
Will they live in the hostel?
Yes, they will. No, they won’t
They won’t live in the hostel.
Where will they live?
They will live in the hostel.
Who will live in the hostel?
They will live in the hostel.
The Future Indefinite Tense
Adverbial Modifiers of Time
Exercise 1. Express your agreement with the following statements: Use the phrases:Certainly. It is really so. You are right . I agree with youas in… - My brother is going to become a University student next…Exercise 6. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
1.They will attend experimental shops next month. 2. I’m sure he will be a good specialist in future. 3. The students will have a good time together at the weekend.The Indefinite Tense (Review)
I study at the University. My brother studied at the University 5 years ago. Ann will study at the University next year. …III. Reading and comprehension
Look through Text A. be ready to answer the following questions: 1.Do you work or study?Text A
Student’s Life
I study at the Kherson State Technical University, the department of Cybernetics. In summer I passed all my exams successfully and my dream to become a student finally came true. But there were many young people who failed their entrance exams. My friend for example failed in mathematics. It wasn’t really his fault, it was just bad luck. He will try again next year.
And now I am going to tell you about my family. My father’s name is Sergei Petrovich, he is 47. He works as a surgeon at a hospital. He is neither old nor young. He is a good-looking man, handsome, rather thin with dark brown hair just beginning to grey. He is a very sociable person. What I don’t like about my dad is that he is always busy. Very often he works overtime. He is a bread-maker in our family. He is fond of going to the country at the weekend, because he enjoys working in the garden. My mother’s name is Galina Nickolayevna. She is 46. She works as a teacher at a nursery school. My mother is rather slim and pretty, she is always elegant and smart. She always has a lot of work to do both school and about the house. I have neither sisters nor brothers. But I have a lot of relatives-grandmothers, grandfathers, great-grandparents and cousins.
I was much interested in physics at school. I studied it at the school physics circle. I was also fond of literature and used to write poems. I didn’t know what to choose: physics or literature. I finished school and began to work on the farm. Then I served in the army. After that I worked as a machine operator at an engineering plant. I worked there for two years and decided to enter the University. It took me rather long to get used to University life. To be quite honest I never knew I was so much behind the others. It will take me months of real hard work to catch up with the fellows. I think I won’t be disappointed.
My lessons usually begin at 8 o’clock and I get up very early because I live far from the University. It takes me an hour to get there in time. Those students who live in the hostel are lucky it take them only a few minutes to get there. I live with my parents in a new comfortable apartment. Our monitor and Trade Union organizer live in the hostel. Now I compare the life at home with my parents and in the hostel.
We do many subjects at the University. Here are some of them: physics, higher mathematics, foreign languages (English, German, French, Spanish ), history of Ukraine. I like the history of our country most of all, because there are still so many facts which I want to know. We take credits and examinations twice a year in January and in June. Our lessons end at 3 o’clock. I usually go home by bus or work in the library or in the physics laboratory. I shall study hard to get education and to become a good specialist. My group-mates and I will try to find time for some enjoyment as well. There will be a sport competition at the end of the term and I hope I shall take part in it.
IV. Practice
Student’s Biography The Past Indefinite Tense The Present Indefinite Tense The Future Indefinite Tense … (+) V2 (ed); was ,were (+) V(V(e)s); am, is, are (+) will V(am, is, are going to).Personal Information Sheet
First name ____________________
Last name ____________________
Date of birth _____________________________________________
(month) ( day ) ( year)
Nationality ____________________
Place of Birth ______________________
Citizenship ________________________
Permanent address ________________________________________
Phone _________________
Education ______________________
 Secondary school
Secondary school
 Professional school
Professional school
 Technical school
Technical school
 Lyceum
Lyceum
Year of leaving ______
Languages:

 Russian Excellent Good Fair
Russian Excellent Good Fair

 Ukrainian Excellent Good Fair
Ukrainian Excellent Good Fair

 English Excellent Good Fair
English Excellent Good Fair
Marital status:
 Single
Single
 |
Married
 Divorced
Divorced
 Widowed
Widowed
Date ____________________________
Signature ___________
Exercise 3. Role play the situations:
Situation 1.
Guide words: not far from the University, a floor with a special reading –room and recreation hall, to gather in the evening, to listen to music, to…Situation 2.
1. Your friend thinks the examinations will be easy. You disagree with him (her) giving your reasons.
Guide words: I think this subject is your weak point ,to fail in exam, to sit for an exam, to have little time, difficult to learn, difficult to remember, to study together, to study hard.
Situation 3.
1. Your friend will leave school next year. He wants to enter the same University where you study. You tell him about the student’s live.
Guide words: entrance exams, to be an applicant for entry, to take a preparatory course, tutorials, instructions, laboratories , to do well, to be good at, to go in for sports, scholarship, to have a good time, to celebrate a holiday .
Situation 4.
1.You are on practice at a foreign enterprise. The head of the enterprise is interested in your personality. Tell him about yourself .
Situation 5.
1.You ,a Ukrainian student, meet at the Club of International Friendship of your city a foreign student. He asks you about your life, family, childhood.
Guide words: to be born in, to enter the University, to study at the department of, to live at home (in the hostel), parents, to work as, to go in for sport, to attend computer courses.
V. Reading
Leisure-Time Activities (My Days Off and Holidays )
Even if we all have different ideas about an ideal holiday, we all have to face two problems: time and money. On weekdays I usually go to the University but on my days off I prefer to… We are fond of picnics chiefly because we have an excellent opportunity to admire the beauty of nature and have a bite…Word List
to go climbing ― займатися альпінізмом to face the problem ― зіткнутися з проблемою leisure ― дозвілляSupplementary Reading
abdication ― отречение • зречення enthusiasm ― увлечение • захоплення to make one’s broadcast ― выступать в радиопередаче • виступати у радіопередачіRead the texts, give a summary and discuss them.
The Royal Family
As a child she studied constitutional history and law as well as art and music. In addition she learned to ride and acquired her enthusiasmfor… The marriage of the young Princess Elizabeth to Phillip, Duke of Edinburgh… Among Queen Elizabeth’s many duties are Commonwealth, whose interests and welfare are very important to her. The Queen…The Royal Family
From the reign of King George VI up to September 1990
King George VI
1895 –1952.m. Lady
Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon
(Queen Elizabeththe Queen mother)
Queen Elizabeth II Princess Margaret
b.1926 b.1930, m. Antony
m. Philip, the Earl of Snowdon
the Duke of Edinburgh(divorced in 1978)
David Lady Sarah
Viscount Linely Armstrong- Jones
b.1961 b.1964
Charles Anne Andrew Prince Edward,
The Prince of Wales Princess Royal The Duke of Yorkb.1964
b. 1948 m. Lady b. 1950, m. Captain b. 1960, m. Sarah Ferguson
Diana Spencer Mark Phillips
(divorced in 1989)Princess Beatrice of York, Princess Eugenie of York,
b.1988 b.1990
Peter Phillips, Zara Phillips,
b. 1977 b.1981
Prince William of Wales Prince Henry of Wales
b.1982 b. 1984
Order of Succession to the Throne
Prince William of Wales Prince Henry of Wales The duke of YorkAlexander Bell-the inventor of the telephone
Marie Curie
Once in Paris Marya began a course of hard study and simple living. She decided to work for two Master’s degrees ― one in Physics, the other… Among many scientists Marya met and worked with in Paris was Pierre Curie.… Pierre Curie and Marya Sklodovska , both of whom loved science more than anything else, very soon became the closest…Notes
a teacher of science ― преподаватель естественных наук (химия физика биология)
master’s degree ― учебная степень магистра
under this hard mode of life ― при такой тяжелой жизни
a Bachelor of Science ― бакалавр естественных наук (звание присваиваемое после окончания университета
spare him a very meager salary ― (зд.) платило ему мизерное жалованье
A)Read the text and find our how the British like to spend their free at home
Recreations
Watching television is a very popular leisure pastime in Britain. A typical day’s viewing includes film. Plays, current affairs, light… Lost of people enjoy “soap operas”. Coronation Street, Crossroads East Enders,… The growth in use of videocassette recorders and equipment (including home computers) for playing television games has…I. Language
Sentence Patterns
Key examples to be memorized
|
Illustrative Examples
He is working at his invention.
Is he working at his invention?
Yes, he is. No, he is not.
Is he working or studying?
He is working.
What is he doing?
He is working at his invention.
What invention is he working at?
He is working at the development of a new device.
Where is he working at his invention?
He is working at his invention at the scientific research institute.
II. Grammar
Дія в процесі, відбувається в момент мовлення Affirmative (+) …Exercise 1. Open the brackets using the verbs in the Present Continuous.
1. The boy (to run) about in the garden. 2. John and his friends (to go) to the library. 3. Ann (to sit) at her desk. She (to study) English. 4. A…Exercise 2. Open the brackets using the verbs in the Present Indefinite or the Present Continuous.
III. Practice.
He is speaking English. Is he really speaking English? Model:Exercise 3. Translate it into English.
1.Куди ти зараз йдеш? 2. Я йду додому, а ти? 3. А я – до університету. Там будуть збори студентів. 4. А де ти був учора, коли я дзвонив тобі? 5. Я ходив на пошту відправити лист. 6. Ти багато вчив вчора? 7. Так, я вчив англійські слова, робив вправи, але в мене не було підручника і я подзвонив своєму товаришу. 8. А що ти робиш зараз? 9. Зараз я чекаю на свого товариша. Він прийде через декілька хвилин.
III. Reading and Practice.
Read and retell the following text.
A Letter
The weather in Kherson is dull, it is raining now. My parents are at home today. Mother is teaching our Hellen English and father is reading a book… Hope to see you soon. Yours, Peter.V. Language
Sentence Patterns
Key examples to be memorized
|
Illustrative examples
They are going to listen to music.
Are they going to listen to music?
Yes, they are. No, they are not.
What are they going to do?
They are going to listen to music.
VI. Grammar
The structure to be going to do smth.
Передає намір, найближчу, наступну дію
Exercise 1. Translate the following sentences.
Exercise 2. Translate the following sentences into English: 1. Ми збираємося писати контрольну роботу. 2. Вони збираються прийти на іспит вчасно. 3. Вони збираються послухати…VII. Grammar
Numerals
1 000 one thousand (a thousand) 2 000 two thousand 1 000 000 one million (a million)Dates
в 1990 році - in nineteen hundred
в 1909 році - in nineteen nine
in nineteen o (ou) nine
в 1970 році - in nineteen seventy
Слово year ставиться перед числівником: in the year nineteen seventy
17 вересня – on the seventeenth of September
Exercise 1. Read the following numbers:
41, 62, 89, 97, 17, 125, 796, 450, 1820, 25 129, 49 357, 151 583, 1 352 765, 2/3, ¼ , 5/6.
Exercise 2. Translate into English:
a) 9 травня 1945 року, 7 січня 1977 року, 5 серпня 1986 року, до 31 січня 1971 року, в липні 1999 року.
b) 25 км., 175 000 людей, 3 500 студентів, 8790 книг, 3 75 285 машин, 17 слів, 30 годин, 19 кімнат, 90 сторінок, 0,5 кг.
Exercise 3. Make up dialogues about the date, day, year.
Model:- What’ s the day today?
- It is the 6th of October, 1997.
- And what day is it today?
- It’s Monday.
- No, it is not.
- Why?
- Because it was Saturday yesterday.
- Yes, you are right. I’m sorry. It is Sunday today.
Prepositions of time
Exercise 1. Read the poem
Exercise 2. Fill in the prepositions: 1. Don’t come late. Come … nine o’clock. 2. What time is it? It is half ……VIII. Reading an Comprehension
Read and translate the text:
Time
There are twenty four hours in a day. Each day begins with sunrise and ends with sunset. The time of the sunrise is morning and the time of the sunset is evening. Morning is the time between sunrise and the noon. Noon is twelve o’clock in the daytime. Sometimes we call it midday. Afternoon is the time between twelve and five or six o’clock in the evening. Then comes evening and night. Twelve o’clock at night is midnight. People have a clock or a watch to tell the time. There are 60 minutes in an hour and there are 60 seconds in a minute. Half an hour equals 30 minutes. A quarter of an hour equals 15 minutes.
What is the time? – Котра година?
It is nine o’clock – Дев’ять годин
It is half past nine. – Пів на десяту
It is a quarter past nine. - Четверть на десяту
It is five past nine. – П’ять хвилин на десяту
It is ten (minutes) to nine . – Без десяти хвилин дев’ять
It is a quarter to nine. – Без четверті дев’ять
My watch is fast . – Мій годинник спішить
My watch is (five minutes) slow. – Мій годинник запізнюється на п’ять хвилин
My watch is correct. – Мій годинник йде правильно
It is ten sharp. – Рівно десять.
IX. Practice
It’s five o’clock. It’s ten past five. Model:X. Language
Sentence Patterns
Key examples to be memorized.
|
Illustrative Examples
It is cold.
Is it cold? Yes, it is. No, it is not cold today. It is warm.
What time is it? It is five o’clock.
What date is it today? It is the 7th of February.
What day is it today? It is Monday.
What month is it? It is October.
Is it far from there? No, it is not. It is near. It is easy to get there.
Vocabulary to be learnt
Grammar
It is easy is difficult is impossible to get thereXI. Practice
Exercise 1. Express your surprise and give short affirmative (negative) answer as in the model.
1. It is rainy in November. 2. It is easy to learn French. 3. Is it warm in… Exercise 2. Object to the sentences. Use the phrases: No, it is not so. I’m afraid you are wrong. I can’t agree with…Exercise 3. Translate into English.
1. В кімнаті холодно. 2. Тут темно. 3. Тепло. 4. Цікаво читати цю книгу. 5. Зараз йде дощ. 6. Взимку часто йде сніг. 7. Мені важко перекласти цей текст. 8. Необхідно прочитати цю статтю. 9. Неможливо зрозуміти, що він хоче сказати.
Grammar.
Degrees of Comparison of Adjectives and Adverbs
not so … as - не такий … як ,( не так …як) the more …. the better - чим більше … тим кращеXII. Reading and Comprehension
Read and translate the text.
The Seasons and the Weather
Winter usually begins in December and ends in March. It is cold in winter and it often snows. There is much snow on the ground. It gets dark early… But winter is a good time for sports. In winter we can go in for such kinds of… Spring comes at the end of March. The sun begins to shine more brightly, the days become longer and the first spring…Read the poem by Robert Burns
The flowery Spring leads sunny Summer,
And yellow Autumn presses near,
Then in his turn cmes gloomy Winter,
Fill smiling Spring again appear.
XIII. Practice
1) - What is the weather like today? - Very cold, the temperature is well below zero, a very chilly wind is… - I am not going out that case. I hate cold.I. Language
Sentence Patterns

Key examples to be memorized
Illustrative Examples
Ukraine is washed by the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
Is Ukraine washed by the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov?
Yes, it is. No, it isn’t
Ukraine is not washed by the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
What is Ukraine washed by?
Ukraine is washed by the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
Vocabulary to be learnt
Grammar
Passive Voice
Active Voice Passive Voice Present Indefinite Tense The Black Sea and the Sea of Azov wash Ukraine.… Переклад дієслів в Passive Voice на українську мовуExercise 1. Give Passive transformation of the following sentences as in the models. Translate the sentences.
1. The Dnipro divides Ukraine into two parts: Right-Bank and Left Bank… 2. The teacher showed students many colourful slides of Kiev.Exercise 2. Make up sentences of your own using the suggested words. Use the Passive Voice.
1. The Independence of Ukraine – to proclaim – August 24,1991Exercise 3. Study the verbs with prepositions. Translate the sentences given below into Ukrainian.
to insist on (upon) – наполагати на to look at – дивитися на to take care of – піклуватися проExercise 6. Express your surprise and give short affirmative (negative) answers as in the Model .
1. The liberation war of Ukrainian people in 1648-1654 was headed by Bogdan Khmelnitsky.Exercise 6. Ask your friend all possible questions to the following sentences.
1. State power in Ukraine is based on the division of the power into legislative,Exercise 7. Say it in English.
1. Величезна кількість цукрового буряку, картоплі, соняшника вирощується на Україні.
2. Президента України обирають строком на 5 років.
3. Нам запропонували відвідати деякі історичні місця Києва.
4. Всі предмети в навчальних закладах України викладаються українською мовою.
5. Майдан Незалежності було реконструйовано в 2001 році.
6. День Конституції України святкують 28 червня.
III. Reading and comprehension
Look through Text A about geographical position of Ukraine. Be ready to answer the following questions:
1. What is Ukraine’s population?
2. What area does Ukraine cover ?
3. What countries does Ukraine border on?
4. What seas is Ukraine bounded by?
5. What makes Ukraine ideal for the development of agriculture?
6. What river divides Ukraine into two parts?
7. What are the main industrial centers in Ukraine?
Repeat after the speaker. Learn the words.
to be criss-crossed - перехрещувати to ensure - забезпечувати, гарантувати highways - автошляхиText A
Geographical position of Ukraine
Ukraine covers about 603.700 sq.km being larger than any country in Western Europe. It borders on Belarus and Russia in the north and in the east.… Ukraine is in an ideal geographical position for the development of its… The main part of Ukraine is located in the watershed of the Dnipro River, which divides Ukraine into two parts:…IV. Practice
…V. Reading and comprehension
Read and translate the text B
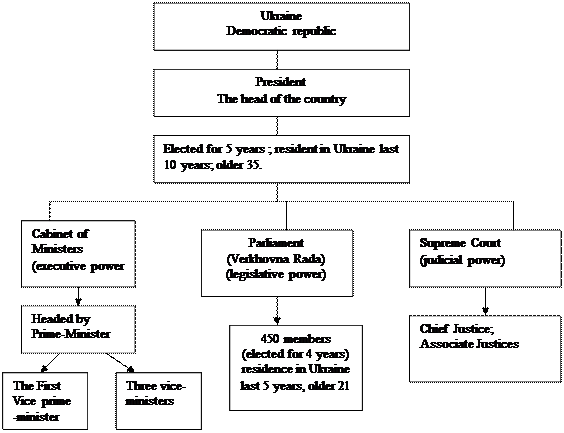
Political System of Ukraine
On December 1,1991, an all-Ukrainian referendum was held , involving 84.18 percent of citizens. Winning 61.6 percent of the votes, L.Kravchuk, the former head of the… In 1994 L.Kuchma won the Presidential elections and became the new President of Ukraine.VI. Practice
Exercise 5. Speak on the topic “Political System of Ukraine” . Use the chart:
 |

VII. Practice
Situation 1.Paula Smith, a British guide of the Ukrainian students in London is going to visit Ukraine. She is interested in information on Ukraine.… Situation 2.A student of the Law faculty is taking an exam in the… Situation 3. A young businessman has a possibility to invest money in the development of our country. He is interested…Exercise 2. Agree or disagree with the following statements
1. Lviv, the historical capital of Galicia and Western Ukraine, and after Kyiv, the second cultural, political, and religious center of Ukraine.
2. By population it is the first largest city in Ukraine.
3. Today Lviv has an area of 200 sq.km.
4. Lviv is the only city in Ukraine that still has some original Renaissance architecture.
5. The main monuments in the city are to Ushakov, T.Shevchenko, B.Khmelnitsky.
Exercise 3. Ask questions to get these answers.
1.In the mid-13th c.
2. St. Nickolas's Church.
4. Vysoky Zamok.
5. Renaissance architecture.
6. To A.Mickiewicz, I.Franko, V.Stefanyk, I.Fedorovych.
Exercise 4 . Put the sentences of the text into the logical order. Retell the text.
2. The most imposing part of Lviv includes Shevchenko prospect, Mickiewicz square, and Horodetska street. 3. Today Lviv has an area of 155 sq km. 4. The oldest monument in Lviv consists of the foundation and walls of St. Nickolas's Church.Exercise 5. Tell about any Ukrainian city which you have ever visited.
IX . Supplementary
Text D The Constitution of Ukraine
On the 24th of October, 1990, the constitutional commission was appointed by the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. The draft constitution was written… The power in Ukraine belongs to people. It is exercised through democratic…Text E Ukrainian Music
The best representatives of the Ukrainian musical culture were well-known artists as the conductor 0. Koshyts, the singers S. Krushelnytska, M.… The Drama Theatre (1882) greatly influenced the development of Ukrainian… The choir activities of M Lysenko, which continued during almost his entire musical career, played an important part…Text F Ukrainian literature
Interest in folklore and ethnography is represented in the works of Levko Borovykovsky (1806—-1889) and Ambros Mellynsky (1814—1870), poets of the… With the founding in the 1830s of a University in Kyiv, the capital became… The poet Taras Shevchenko was the great figure of Ukrainian romanticism, which predominates in the dramatic works of…Text G Science and technology in Ukraine
Ukraine has contributed many outstanding scientists to the world. In the 15th-17th centuries they were the talented physician Yury of Drohobych and… Ukrainians are also proud ofthe fact that only several months after the… The world famous Ukrainian scientists are Volodymir Vernadsky and Yevhen Paton.Exercise 1. Vocabulary to be learnt
II. Practice
Each session of Parliament is usually opened in the House of Lords by the Queen (King). Exactly so. Each session of Parliament…Exercise 3. Express your surprise and give short affirmative (negative) answers as in the Model.
1. There are high mountains in Great Britain .Exercise 4. Ask your friend all possible question to the following sentences. Mind tenses.
1. Britain has the largest energy resources in the European community. 2. In 1967 reserves of natural gas were discovered in the North Sea. 3. Britain has to import many raw materials from abroad.Exercise 5. Say it in English .
2. Найхолоднішими частинами з усіх є високогір’я Шотландії. 3. Темза – найглибша річка Англії. 4. Королева призначає прем’єр-міністра.III. Reading and Comprehension
Exercise 1. Repeat after the speaker. Learn the words
Exercise 2. Look through Text A “ The United Kingdom. Geography and Climate” . Be ready to answer the following questions: 1. What seas is Great Britain washed by? 2. What is Great Britain separated from the continent by?Text A
The United Kingdom. Geography and Climate
The west coast is washed by the Atlantic Ocean and the Irish Sea, its east coast – by the North Sea, and the south coast – by the English Channel,… England is the southern and central part of Great Britain. Scotland is in the… Mountains are an important part of the geography of a country. The British Isles have no high mountains. Scotland is a…IV. Practice
Exercise 1. Using the chart of Great Britain (territory, location, population, parts, etc.) Make a report on the topic.
 |
V. Reading and comprehension
Read and translate Text B
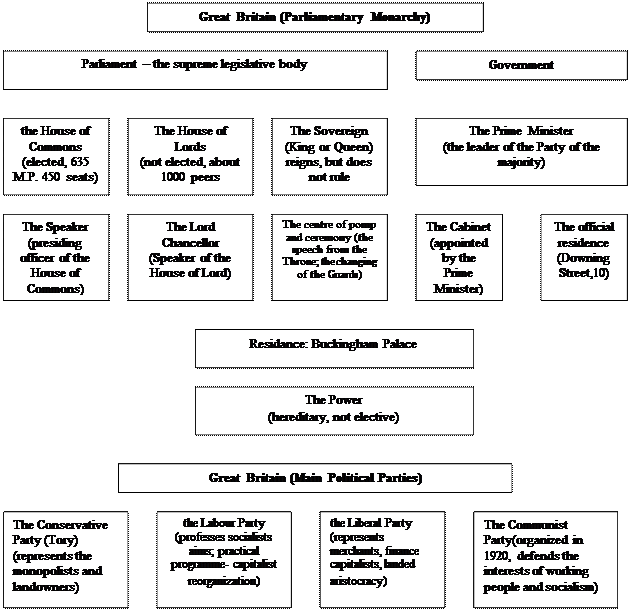
The Government of Great Britain
The legislative power is vested in the Queen and Parliament made up of two Houses – the House of Lords and the House of Commons, the supreme… There is no written constitution in the country. The term “English… As a rule the Prime Minister is the leader of the party that has won the election and has the majority in the House of…Exercise 3. Agree or disagree with the following statements
2. The Parliament limits the powers of the Queen. 3. The Cabinet is headed by the Queen. 4. The Queen and the Parliament exercise the legislative power.VI. Practice
Exercise 5. Study the chart “Great Britain” (Parliamentary Monarchy and Political Parties) and discuss information in the form of questions and answers.
 |
VII. Practice
Situation1.You are invited to take part in the discussion about Great Britain. Make a report on political life of the country. Describe your own… Situation 2. You are in the plane flying from Ukraine to Great Britain. Ask… Usefull expressions:You should see – Вам треба було б подивитись … May I give you some suggestions? - Можна я дам вам…VIII. Reading
Listen to the text C. Be sure that you know the following words and word combinations.
aero-engine manufacturers – виробники авіадвигунів branch – галузь domestic demand - внутрішній попитText C
Great Britain is known to be a highly developed industrial country. There are so-called “old” branches of industry which appeared in the period of industrial revolution and “modern” branches that appeared only after the Second World War.
Coal-mining is said to be a traditional , “old” branch of industry. It is to be found in Wales, in the Cumberland Mountains, in the south of Scotland, and in the northern part of England.
Metal industry, including production of steel and non-ferrous metals such as aluminium and other colour metals, is known to have been developing in Scotland, Liverpool, Manchester, Birmingham, Sheffield, in Wales and other areas of the country.
Britain’s chemical industry is the third largest in Europe . Nearly half of its production is exported. Natural gas is known to be a good raw material for chemical industry. Chemical industry, especially production of synthetic fibres and plastics, is being developed on a large scale in Wales, in Liverpool, in the mouth of the Thames, in Scotland, in the south of England.
Engineering is the main branch of industry in Great Britain. Britain is the Western world’s largest producer of agricultural tractors, many of which are exported. London, Birmingham, Coventry are known to be the most important centres of motor-car construction. The Greater London, Bristol are the leading centres of aviation industry. The British aerospace industry is the third largest in the world. Its products include civil and military aircraft and satellites. Rolls-Royce is one of the world’s three largest aero-engine manufacturers. Glasgow, Newcastle, Belfast are the biggest ship-building centres.
Among the modern branches are electroengineering, electronic, machine-tool industries which can be found in the Greater London, Leeds, Sheffield, Manchester, Birmingham, Liverpool and many other big and little towns of Great Britain. Halifax is known to be a machine-tool construction centre producing equipment for electric power industry.
Textile industry with the centres in Yorkshire and Landshire is considered to be one of the oldest in Great Britain. The clothing industry, one of the largest in Europe, meets about two-thirds of domestic demand and the woolen industry is one of the world’s largest.
Light industry and first of all clothing, footwear, knitting wear and hosiery are developed in Leeds, Nottingham, Manchester, London, Glasgow, Belfast. Light industry goods are of good qualty.
Nottingham, Lester and Derby are known to be the most important centres of footwear industry. Many enterprises of food industry are situated in the large industrial centres such as London, Belfast, Liverpool, Bristol as well as in other centres and also in some rural areas.
Britain has an open economy in which international trade plays a vital part. About one-quarter of its domestic product comes from the export of goods and services.
IX. Comprehension.
Exercise 1. Find the right ending of the sentence.
a) textile industry b) metal industry including production of steel and non-ferrous metal c) aerospace, electronic and machine tool industriesExercise 4. Make a chart of the development of industry in Great Britain and speak on the topic.
X. Supplementary
Text A
Science and Technology
Spending on scientific research and development in 1988 was about £10,300 million, 2-2 percent of gross domestic product. The Government takes… The Science and Engineering Research Council supports fundamental research in… The Medical Research Council supports major projects in all types of disease, including Alzheimer's disease and AIDS.…Text B
The Arts
The British Council furthers knowledge of British culture and the English language overseas. It initiates or supports tours by British companies and… London is a major international centre for theatre, opera and dance. There are… British pop musicians and groups have worldwide appeal and have set new trends.Text C
London Museums and Art Galleries
The British Museum in Russel Square comprises the National Museum of Archeology and Ethnography, the richest collection of prints and drawings and… It was founded in 1753 and opened to the public on the 15th of January,… The Library of the British Museum is one of the largest collection of books and manuscripts (pyкописи) in the world. …Text D
Sport and Recreation
Britain has pioneered facilities for sports for disabled people. Disabled athletes are encouraged to participate either in direct competition with… Wimbledon, one of the four grand slam tennis tournaments, is the world's… In 1990 England were World Cup soccer semi-finalists. The Government has worked closely with the football authorities…I. Language
Sentence patterns
|
Illustrative examples
I cannot speak English Can I speak English? Yes, you can. No, you cannot (can’t)Grammar
Modal Verbs and their equivalents
Exercise 1. Practice the following table. Translate each sentence into Russian or Ukrainian
Exercise 2 . Express your agreement with the following statements. Use the… He can go to Kyiv for the week-end Surely, he can go to Kyiv for the week-end …Exercise 3. Express your surprise and give short affirmative (negative) answers as in the model.
1. He can put his bag in the left luggage box. 2. You can invite your friends to join us.Exercise 6. Express your surprise and give short affirmative (negative) answers as in the model.
1. We may part with them just now. 2. I may call him any time I like.Exercise 9. Express your surprise and give short affirmative(negative) answers as in the model.
1. You must see Nelson’s Column in Trafalgar Square. 2. They must exhibit Russian painting at National Picture Gallary.Exercise 11. Ask your friend all possible questions to the statements.
1. English people must drive on the left side of the road.
2. You can travel to Kyiv both by train and by plane.
3. She may read the immortal “Tale of Bygone Days” in our library.
4. After restoration tourists can visit the Golden Gate – the ancient entrance to Kyiv.
5. Industrial potential of Kyiv must develop day by day.
6. Masterpieces of architecture in Kyiv must impress you greatly.
II. Language
Sentence Patterns
Key examples to be memorized
|
Illustrative examples
We have been to the South this year.
Have you been to the South this year?
Yes, I have. No, I haven’t.
I haven’t been to the South yet.
I haven’t seen him since 1996.
Have you bought this dictionary or taken it from the library?
I have bought it this week.
Where have you bought it?
I have bought it at the book shop in the center of the city.
Who has seen this performance? I have (she, he has)
The Present Perfect Tense
Exercise 1. Make up sentences using the table. Pay attention to the place of the adverb and adverbial modifiers of the time in the sentence.
The builders have painted Kyiv National University red. It is really so. They have painted Kyiv National University red. … 1. Fifteen centuries have already passed over Kyiv ancient hills.Exercise 3. Express your surprise and give short affirmative(negative) answers as in the model.
1. Higher educational establishments have changed their status since 1990. 2. Kyiv theatres have already staged a lot of modern plays by R.Viktyuk. 3. I hope you have seen these slides about London.Exercise 5. React to the following questions
2. Which of the well-known places of interest in Kyiv has impressed you most? 3. Has she managed to visit all the best museums in London? 4. What city has made you feel at home?Exercise 6. Translate the sentences from Ukrainian into English.
2. Кому пощастило відвідати Ковент Гарден у Лондоні? 3. Клерки, адвокати, судді жили і працювали, навчались у Inner Temple, Middle… 4. Хто це презентував тобі такі гарні вироби з напівкоштовних металів?I. Reading and Comprehension
I am a student of KSTU. I must write a composition about my summer holidays. This summer I have been to Kyiv and this city has impressed me greatly. I have… Kyiv, the capital of Ukraine is the largest city in Ukraine with the population about 3 million. It’s a political,…Exercice 1. Give Ukrainian equivalents for the following
- furthermore - immortal - cellExercise 3. Answer the following questions
2. Has Kyiv impressed you greatly? 3. What did you like most? 4. What is the population of Kyiv?II. Practice
Exercise 4. Try to find out the way to certain places. Do it as in the Model.
- to Russian Art Museum - to St.Sophia CathedralExercise 5. Say it in English
2. Це місто відсвяткувало 1500 річницю в 1982 році. 3. Ярослав Мудрий заснував Софіївський собор в 1037 році. 4. Хрещатик завжди був головною магістраллю Київа.Exercise 7. Role-play the following situations
Situation 1. An English student has just come to Kyiv on summer holidays. He is eager to know about the city. He asks Ukrainian students about educational institutions, industrial enterprises, historical centres.
Situation 2. You are a representative of the Ukrainian touring company in London. Speak about wonderful opportunities to visit historical places of Kyiv and a nice cultural program. Your Londoners ask you questions about Kyiv.
III. Reading
Impressions of London
Dear Galina! Here I am in London on a fine summer morning. Have you received my post-card?… I’ve never before lived in a big city, so London is a new world for me, and I’m going to find out more about it. What…Exercise 5. Say it in English
2. Вчора я оглянув деякі визначні місця. 3. Ви коли-небудь були в Національній Галереї? 4. Він багато читав і чув про перемоги адмірала Нельсона у війні проти Наполеона.IV. Practice
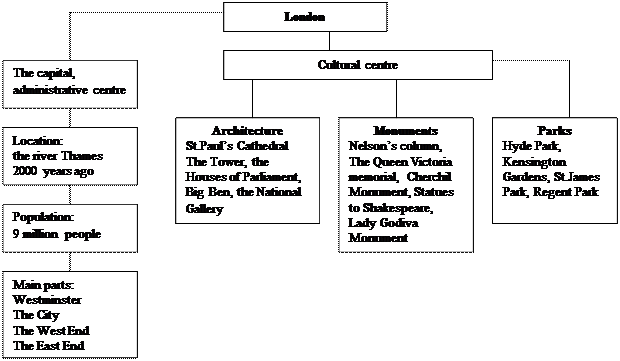
Exercise 1. Speak on the topic “London, the capital of UK”. Use the chart.
 |
Exercise 2. Make up dialogues using the chart.
Exercise 3. Role-play the following situations:
Situation 1.You are at the student’s club. Share the impressions of your tour of London with the members of this club.
Situation 2. You have come to London on a 6 day visit. Discuss your plans of visiting places of interest.
V. Reading and comprehension
Exercise 1. Read the text “Kherson” and translate it.
Kherson
Tomorrow I’ m going to write a letter to my new friend John. I have looked through some books, guide books, inguiries about Kherson and I think I… Kherson is a regional centre of the south of Ukraine with the population of… Kherson was founded in 1778 as a fortress to defend Russian lands from Turkey by the order of Empress Katherine II.…VI. Practice
Exercise 5. Try to find out the way to certain places. Use the words given below. Do as in the model.
Expressions: go straight ahead, second turning, turn to the right, on your left, quite a distance from here, round the…Exercise 7. Make up dialogues about Kherson using the chart
Exercise 8. Role-play
Situation 1.Suppose you are a guide. Tell the tourists about the most interesting places of interest of interest in Kherson. Answer their questions.
Situation 2.Your friend from Poltava has come to Kherson. He wants to enter one of our Universities. He is also interested in industry where he can work after the graduation. Advise him the university worthly to enter and industry developed in our region.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
BRITISH HOLIDAYS AND LONDON PAGEANTRY
In England and Wales they comprise at present five bank holidays (New Year's Day, Easter Monday, spring and late summer holidays at the end of May…January , 1
New Year's Day
It is a bank holiday though many Britons do not celebrate on New Year's Eve. In Scotland New Year's Eve is called Hogmanay and is an occasion for joyous celebration. In London Scottish people gather on the steps of St. Paul's Cathedral and sing "Auld Lang Syne" at midnight.
April, 3
Easter
The word Easter owes its name and many of its customs to a pageant festival hold eostre which is the name of the Anglo-Saxon goddess of spring time. Every spring European peoples celebrated the festival to honour the awakening of new life in nature.
Christians related the rising of the sun to the resurrection of Jesus and their old spiritual rebirth. This "holy" day is celebrated in many countries of the world.
Spring and Summer Bank Holidays
The Summer Bank Holiday is the most popular holiday, because it comes at a time when children are not at school. Many families try to go away to the seaside or the country as they may indeed have done at Easter or in Spring.
November, 11.
Remembrance Day
This day is observed throughout the Commonwealth and dates back to November 11, 1918 when all fighting in the First World War ended. It now commemorates British soldiers, sailors and airmen who gave their lives in the two World Wars. Special services are held and wreaths are laid at the Cenotaph, a war memorial at Whitehall, where thousands of Londoners observe the two-minute silence and participate in the remembrance ceremony. Similar ceremonies are held throughout the country.
December, 25.
Christmas
* * London remains one of the world's strongholds of pageantry much of which is…Trooping the Colour
The State Opening of Parliament
This is another royal event at the end of November which draws thousands of spectators, who see the Queen on the drive from Buckingham Palace to the Houses of Parliament in the State Coach. The public are not admitted to Parliament to see her read the speech from the Throne, prepared for her by the Government. But the State Opening since 1966 is televised. Visitors are admitted to the Public Galleries only by the personal invitation of the members of Parliament.
CHIEF PUBLIC HOLIDAYS IN THE UNITED STATES
Americans share some holidays such as Easter, Christmas and New Year's Day with other countries of the world. Here are public holidays which are… January,1 New Year's DayMemorial Day
This day was first established to honour the dead in the war between the North and the South, a mournful remembrance of the fallen.
July, 4.
Independence Day
This is the most important holiday of the nation, which celebrates Ms birthday. On this day in 1776 the Continental Congress adopted the famous Declaration of Independence declaring the former British colonies free, thus founding the United States of America.
October, 19.
Columbus Day
Christopher Columbus, an Italian, discovered the American continents in 1492 by accident, while seeking a short route to Asia. Thus, he called the natives the Indians and the islands he explored, the West Indies which bear these names to this day. This event is widely celebrated in most Latin American countries as well. The District of Columbia was named in his honour as well as many cities, squares and streets.
November, 11.
Veteran's Day
This day, like Memorial Day, is a solemn occasion in honour of all American veterans of all wars. In many communities veterans march in parades, national flags are displayed, special ceremonies, observing two minute's silence, are held at the tomb of the Unknown Soldier in Arlington National Cemetery.
November, 24.
Thanksgiving Day
It is the oldest national holiday. The pilgrims, the first English settlers searching for religious freedom, came on May/lower to Plymouth Bay, Massachusetts, in 1620. They suffered a very hard year. By the autumn of the next year assisted by the Indians they had a good harvest. And a feast was given of turkey corn and pumpkin pie to celebrate the harvest and give thanks to God for their survival. The old traditions of their feast are observed throughout the country today.
December, 25.
Christmas
Christmas is a great American and British festivity, very rich in custom and tradition — with Santa Claus, the decorating of the Christmas tree, of card sending and gift giving. It is celebrated as the birthday of Christ. Now it is becoming more and more a folk holiday. It has always been observed as a family affair.
LIST OF IRREGULAR VERBS
BASE FORM PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
Verbs which are the same in all three forms
cost cost cost
cut cut cut
hit hit hit
hurt hurt hurt
let let let
put put put
set set set
shut shut shut
Verbs which have the same form for Past Simple and Past Participle
bring brought brought build built built burn burnt burntVerbs which nave the same form for the Base Form and the Pats Participle
become became become
come came come
run ran run
One verb which has the same form for the Base Form and the Past Simple
beat beat beaten
Verbs which have all forms different
begin began begun bite bit bitten blow blew blownУрок 1
Читання голосних в наголошеному складі
| Голосна | Відкритий | Закритий | Закритий з буквою r | Відкритий Гол.+ r + гол. |
| A, a | [ e i ] make | [ 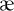 ]
bad ]
bad
| [  ]
bar ]
bar
| [ 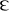  ]
fare ]
fare
|
| E, e | [ i: ] be | [ e ] pen | [  : ]
her : ]
her
| [ i ]
mere ]
mere
|
| I, i | [ a i ] Mike | [ i ] fill | [  : ]
first : ]
first
| [ ai ]
fire ]
fire
|
| U, u | [ j u: ] mute | [ 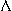 ]
bus ]
bus
| [  : ]
burn : ]
burn
| [ju ]
pure ]
pure
|
| O, o | [  u ]
no u ]
no
| [ 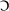 ]
not ]
not
| [ 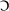 : ]
port : ]
port
| [ 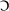 : ]
bore : ]
bore
|
| Y, y | [ a i ] type | [ i ] system | [  : ]
myrtle : ]
myrtle
| [ ai ]
tyre ]
tyre
|
Ex.1. Прочитайте слова і поясніть їх правила читання
Vote, probe, fine, be, lake, me, pen, bad, an, tube, tunnel, plan , hat, bit, mute, nut, pane, tub, mud, leg, mode, pit, go, did, hate, and, spoke.
Ex.2. Прочитайте слова:
- [ 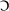 ] pod, loss, hot, soft, top, solve, rod, spot
] pod, loss, hot, soft, top, solve, rod, spot
- [ 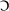 : ] port, born, form, sort, pork, storm, ore, more
: ] port, born, form, sort, pork, storm, ore, more
- [ j u: ] tune, tube, lute, mute, due, use, duty, fume
- [ 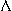 ] hum, sum, must, sun, plus, nut, dust, bulb, mud, bus, hunt
] hum, sum, must, sun, plus, nut, dust, bulb, mud, bus, hunt
- [  : ] burn, first, turn, term, fur, firm, stern, burst
: ] burn, first, turn, term, fur, firm, stern, burst
- [ i ] pit, lift, miss, mill, list, pink, tin, drill
- [ ai ] like, type, fine, dyne, wide, style, spike, life, mine
- [  ] mark, spark, are, dark, park, army, harm, bar
] mark, spark, are, dark, park, army, harm, bar
- [ e i ] state, date, rate, tame, lake, base, take
Ex.3. Розмістіть слова по групам в залежності від читання букви a :
Park, lane, lad, plate, spare, spark, rate, rare, pare, add, hard, farm, bare, make, flat, brake, band, start, fare, tank, land.
Контрольна вправа
Bed, lift, same, hand, sun, tune, try, free, fur, flat, born, spare, mute, try, my, note, pole, burn, mass, plus, dark, dare, bark, stone, spire, hide, home, wire, wore, study, hard, style, wide, type, store.
Читання приголосних c, g, s, x
Ex. 1. Прочитайте наступні слова: - [ s ] mice, dress, ice, rice, cent, sent, see, sport - [ z ] has, rise, bags, pens, his, tables, diesУрок 2
Читання голосних “і” та “y”
| i + ld, nd, gn, gh | ia, io | ir, yr | y/i + r + e |
| [ ai ] | [ ai ] ]
| [  : ] : ]
| [ ai ] ]
|
| mild find sign light | via ion bias dial | first third myrtle thirst | fire tyre wire tired |
Ex.1. Прочитайте наступні слова:
- [ ai ] child, wild, grind, mild, kind, find, behind, sign, design, assignment, alignmet, night, bright, fight, high, light, slide, lie, prize, giant, try, type, rely, spline
- [ ai ] fire, bias, dial, trial, violet, spire, wire, tire, spiral, desire, entire, admire, via
] fire, bias, dial, trial, violet, spire, wire, tire, spiral, desire, entire, admire, via
- [  : ] first, third, circle, firm, birth, dirty
: ] first, third, circle, firm, birth, dirty
- [ i: ] symbol, system, crystal, oxygen, plenty, party, easy, energy, carry, ordinary
- [ j ] yes, yet, yoke, yard, yellow, yield, yak, yank, yap, yarn, yaw, yawl, year, yearn, yearst, yelk, yellow, yelp, yen, yoke
- [ i: ] field, brief, chief, piece, achieve, believe
Запам’ятайте:
your [jo:r] science ['saıəns] friend [frend]
young [jΛŋ] give [gıv] live [lıv]
Ex.2. Прочитайте наступні слова і поясніть правила читання букв “i” та “y”
Rise, lie, ride, ring, strike, reside, slight, grid, filament, combine, iron, imagine, incident, divide, velocity, shift, advice, decide, middle, quite, single, circus, final, mankind, fish, differ, bring, rye, syllable, shire, liquid.
Урок 3
Читання букви “a”
| Відкритий склад | Закритий склад | |||||
| ai, ay | a+r+e/ air | a+r; a+th | a+ f, s, n, + | a+u; a+w | a+ l+ приг. | w(h) + a |
| [ ei ] | [ 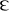  ] ]
| [  ] ]
| [ 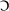 : ] : ]
| [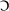 :]/[ :]/[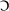 ] ]
| ||
| pain play plait | pair care fare | part fast pass | because August law | all also talk | what was warn |
Ex.1. Прочитайте наступні слова:
- [ ei ] sail, paint, ray, may, railway, train, way, say, mail, retain, raise, pay, lay
- [ 
 ] hair, fair, spare, fare, bare, care, rare, air, dare, airport, prepare
] hair, fair, spare, fare, bare, care, rare, air, dare, airport, prepare
- [  ] arm, alarm, past, class, market, spart, demand, as, basket, plant, draft, fast, last, France
] arm, alarm, past, class, market, spart, demand, as, basket, plant, draft, fast, last, France
- [  : ] small, tall, ball, false, salt, stalk, befall, ward, warn, pause, fault, saw, raw, draw, dawn, lawn, call
: ] small, tall, ball, false, salt, stalk, befall, ward, warn, pause, fault, saw, raw, draw, dawn, lawn, call
Ex.2. Прочитайте наступні слова і поясніть правила читання букви “a”
Care, play, grammar, cage, pair, scare, stairs, ask, atomic, article, advantage, grain, spray, contain, away, assistant, because, besides, aircraft.
Урок 4
Читання буквосполучень sh, ch, th
Ex.1. Прочитайте наступні слова: - [[∫]] shame, shabby, wish, fresh, flash, fish, shadeУрок 5
Читання букви “o”
| oa | o + ld | o+ m,n,th,v | oo | oi, oy | ow | ou | our |
| [ ou ] | [ ou ] | [  ] ]
| [ u: ] | [ oi ] | [ ou] | [ au ] | [au ] ]
|
| load boat goal | old cold hold | love son done | too good book | boy joy oil | grow show low power* | out round sound | our hour |
* - в кінці слова, в інших випадках
Запам’ятайте наступі винятки:
to [ tu ] both [ bou ]
]
do [ du ] over [ ouv ]
]
country ['kntrı] your [ jo: ]
double ['dΛbəl] four [ fo: ]
group [ gru:p ] pour [ po: ]
enough [ı'nΛf] move [ mu:v ]
now [ nau ] cow [ kau ]
how [ hau ] allow [ə'lau]
Ex.1. Прочитайте наступні слова:
[ ou ] - mold, told, fold, golden, old
[ au ] - found, ground, outer, about, amount, profound
[ ou ] - flow, arrow, Moscow, fellow, narrow
[ u: ] - book, look, took, hook, rook, brook, tool, root
[ oi ] - oil, boil, point, toil, toy, boy, avoid, loyal
[ 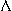 ] - glove, some, come, front, above, month
] - glove, some, come, front, above, month
[ au ] - down, brown, tower, frown, flower
Ex.2. Прочитайте наступні слова і поясніть правила читання “o”
Boil, point, slow, moon, tool, work, other, above, hour, box, copper, doctor, revolve, pore, shore, choose, front, discover, ton, power, around, account, support, force, possible, common, constant, orange, noise, move, country, cool,total, load, ore, coal, road, show, now, become, grow, sound.
Урок 6
Читання буквосполучень wh, ph, gh, qu
Запам’ятайте читання слів: who [ hu: ] whom [ hu:m ]Урок 7
Читання букви “e”
| ee, ea | ie | ea + d, v, th, lth | В позаударному складі | ear + приголосна | ear, eer, e+r+ голосна | ew |
| [ i: ] | [ i: ] | [ e ] | [ i ] | [  : ] : ]
| [ i ] ]
| [ju:]/[u:] |
| feel beam meal feat | piece chief field shield | head heavy breath health | edit enemy medical | heard earth search | ear here mere sphere | new few grew |
Ex.1. Прочитайте наступні слова:
[ i: ] - meet, mean, me, see, he, clean, cheese, cheap, bean, beast, need, peace, beef, believe, peak, beat, sheet, reach, shield, seem, seed, weak, we, wheel, wheat, weep, green, dean.
[ e ] - bed, beg, check, breath, bread, death, feather, dead, fresh, help, thread, heather, wealth, ready
[  : ] - her, term, earth, pearl, heard, earl, earn, hearse, search, serve, stern, reserve, nerve, perch.
: ] - her, term, earth, pearl, heard, earl, earn, hearse, search, serve, stern, reserve, nerve, perch.
[ i ] - fear, ear, dear, bear, here, clear, shear, sheer
] - fear, ear, dear, bear, here, clear, shear, sheer
[ ju: ] - new, stew, dew, screw, pew, Newton, flew, blew, drew,
[ u: ] - clew
Ex.2. Прочитайте наступні слова і поясніть правила читання “e”
Set, serve, heavy, Pete, be, beard, free, here, even, clear, bed, beef, head, eagle, term, egg, lest, she, complete, severe, weep, least, prefer, seem, search, mere, lead, green, get, reserve, nerve, dear, health, theme, defect, emit, heat, defense, death, bread, feel.
Урок 8
Читання буквосполучень ng, nk, kn, gn
[ŋg ] – English, angry, angle, single, mingle, England [ŋk ] - ink, drink, drank, drunk, bank, thank, banker, tanker [n ] – knife, know, knew, knock, knot, knee, knot, knobby, knob, knit, kneel, knag, knack, knick, gnaw, gnomeУрок 9
Читання буквосполучень tion, sion, ture, sure
[t∫ ]– lecture, picture, nature, fracture, temperature, mixture, feature, capture [∫] – fissure, pressure, assure, ensure, fission, session, permission,… [ ]– measure, pleasure, treasure, leisure, measurement, corrosion, provision, television, explosion, occasion.Урок 10
Запам’ятайте читання слів: put [ put ] bush [ bu∫]– Конец работы –
Используемые теги: дисципліни, Іноземна, мова, англійська0.087
Если Вам нужно дополнительный материал на эту тему, или Вы не нашли то, что искали, рекомендуем воспользоваться поиском по нашей базе работ: З дисципліни Іноземна мова англійська
Что будем делать с полученным материалом:
Если этот материал оказался полезным для Вас, Вы можете сохранить его на свою страничку в социальных сетях:
| Твитнуть |
Хотите получать на электронную почту самые свежие новости?







Новости и инфо для студентов